I E Irodov Solutions for Chapter: PHYSICAL FUNDAMENTALS OF MECHANICS, Exercise 3: LAWS OF CONSERVATION OF ENERGY, MOMENTUM, AND ANGULAR MOMENTUM
I E Irodov Physics Solutions for Exercise - I E Irodov Solutions for Chapter: PHYSICAL FUNDAMENTALS OF MECHANICS, Exercise 3: LAWS OF CONSERVATION OF ENERGY, MOMENTUM, AND ANGULAR MOMENTUM
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 1: PHYSICAL FUNDAMENTALS OF MECHANICS, Exercise 3: LAWS OF CONSERVATION OF ENERGY, MOMENTUM, AND ANGULAR MOMENTUM with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Problems in General Physics solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from I E Irodov Solutions for Chapter: PHYSICAL FUNDAMENTALS OF MECHANICS, Exercise 3: LAWS OF CONSERVATION OF ENERGY, MOMENTUM, AND ANGULAR MOMENTUM with Hints & Solutions
A small ball is suspended from a point by a light thread of Iength . Then the ball is drawn aside so that the thread deviates through an angle from the vertical and set in motion in a horizontal direction at right angles to the vertical plane in which the thread is located. What is the initial velocity that has to be imparted to the ball so that it could deviate through the maximum angle in the process of motion?
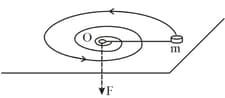
A small body of mass tied to a non-stretchable thread moves over a smooth horizontal plane. The other end of the thread is being drawn into a hole with a constant velocity. Find the thread tension as a function of the distance between the body and the hole, if at the angular velocity of the thread is equal to .
A light non-stretchable thread is wound on a massive fixed pulley of radius . A small body of mass is tied to the free end of the thread. At a moment , the system is released and starts moving. Find its angular momentum relative to the pulley axle as a function of time .
A uniform sphere of mass and radius starts rolling without slipping down an inclined plane at an angle to the horizontal. Find the time dependence of the angular momentum of the sphere relative to the point of contact at the initial moment. How will the obtained result change in the case of a perfectly smooth inclined plane?
A certain system of particles possesses a total momentum and an angular momentum relative to a point . Find its angular momentum relative to a point whose position with respect to the point is determined by the radius vector . Find out when the angular momentum of the system of particles does not depend on the choice of the point .
Demonstrate that the angular momentum of the system of particles relative to a point of the reference frame can be represented as , where is its proper angular momentum (in the reference frame moving translationally and fixed to the centre of inertia), is the radius vector of the centre of inertia relative to the point is the total momentum of the system of particles in the reference frame .
A ball of mass moving with velocity experiences a head-on elastic collision with one of the spheres of a stationary rigid dumbbell as shown in figure. The mass of each sphere equals , and the distance between them is . Disregarding the size of the spheres, find the proper angular momentum of the dumbbell after the collision, i.e., the angular momentum in the reference frame moving translationally and fixed to the dumbbell's centre of inertia.

Two small identical discs, each of mass , lie on a smooth horizontal plane. The discs are interconnected by a light non-deformed spring of length and stiffness . At a certain moment one of the discs is set in motion in a horizontal direction perpendicular to the spring with velocity . Find the maximum elongation of the spring in the process of motion, if it is known to be considerably less than unity.