Jan Dangerfield, Stuart Haring and, Julian Gilbey Solutions for Exercise 10: END-OF-CHAPTER REVIEW EXERCISE 1
Jan Dangerfield Mathematics Solutions for Exercise - Jan Dangerfield, Stuart Haring and, Julian Gilbey Solutions for Exercise 10: END-OF-CHAPTER REVIEW EXERCISE 1
Attempt the free practice questions from Exercise 10: END-OF-CHAPTER REVIEW EXERCISE 1 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Cambridge International AS & A Level Mathematics : Mechanics Course Book solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Jan Dangerfield, Stuart Haring and, Julian Gilbey Solutions for Exercise 10: END-OF-CHAPTER REVIEW EXERCISE 1 with Hints & Solutions
A car is behind a tractor on a single-lane straight road with one lane in each direction. Both are moving at The speed limit is so the car wants to overtake. The safe distance between the car and the tractor is
To overtake safely on the single-lane road, when the car returns to the correct side of the road in front of the tractor there must be a gap between the car and oncoming traffic of at least Assuming a car travelling in the opposite direction is moving at the speed limit, find the minimum distance it must be from the initial position of the overtaking car at the point at which it starts to overtake.
Two hockey players are practising their shots. They are apart and hit their balls on the ground directly towards each other. The first player hits his ball at and the other hits hers at Both balls decelerate at Find the distance from the first player when the balls collide.
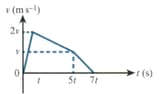
The sketch shows a velocity-time graph for a skier going down a slope. Given that the skier covers during the first stage of acceleration, find the total distance covered.
Two trains are travelling towards each other, one heading north at a constant speed of and the other heading south at a constant speed of When the trains are a distance apart, a fly leaves the northbound train at a constant speed of As soon as it reaches the other train, it instantly turns back travelling at in the other direction. Show that the fly meets the southbound train having travelled a distance of and returns to the northbound train when the train has travelled a distance of
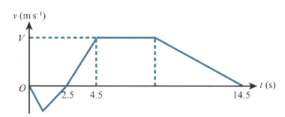
The diagram shows the velocity-time graph for a particle which travels on a straight line where is the velocity of at time The graph consists of five straight line segments. The particle starts from rest when at a point on the line between and and moves towards The particle comes to rest at when
Given that the distance is find the greatest speed reached by during this stage of the motion.
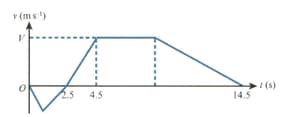
The diagram shows the velocity-time graph for a particle which travels on a straight line where is the velocity of at time The graph consists of five straight line segments. The particle starts from rest when at a point on the line between and and moves towards The particle comes to rest at when
In the second stage, starts from rest at when and moves towards The distance is The particle takes to travel from to and comes to rest at For the first of this stage accelerates at reaching a velocity of Find
the value of
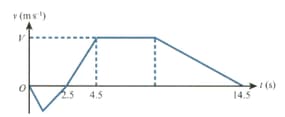
The diagram shows the velocity-time graph for a particle which travels on a straight line where is the velocity of at time The graph consists of five straight line segments. The particle starts from rest when at a point on the line between and and moves towards The particle comes to rest at when
In the second stage, starts from rest at when and moves towards The distance is The particle takes to travel from to and comes to rest at For the first of this stage accelerates at reaching a velocity of Find
the value of at which starts to decelerate during this stage,
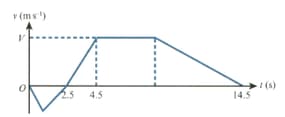
The diagram shows the velocity-time graph for a particle which travels on a straight line where is the velocity of at time The graph consists of five straight line segments. The particle starts from rest when at a point on the line between and and moves towards The particle comes to rest at when
In the second stage, starts from rest at when and moves towards The distance is The particle takes to travel from to and comes to rest at For the first of this stage accelerates at reaching a velocity of Find
the deceleration of immediately before it reaches
