K A Tsokos Solutions for Chapter: Atomic, Nuclear and Particle Physics, Exercise 1: Test yourself
K A Tsokos Physics Solutions for Exercise - K A Tsokos Solutions for Chapter: Atomic, Nuclear and Particle Physics, Exercise 1: Test yourself
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 7: Atomic, Nuclear and Particle Physics, Exercise 1: Test yourself with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Physics for the IB Diploma 6th Edition solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from K A Tsokos Solutions for Chapter: Atomic, Nuclear and Particle Physics, Exercise 1: Test yourself with Hints & Solutions
The graph shows the variation with time of the activity of a radioactive sample,
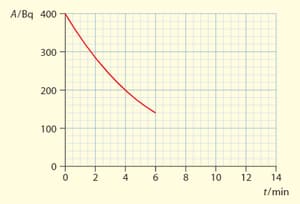
Use the graph to estimate half life of the sample.
The graph shows the variation with time of the activity of a radioactive sample,
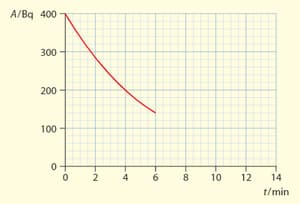
On a copy of graph extend the curve to show the variation of activity for a time up to
The graph shows the variation with time of the activity of a radioactive sample,
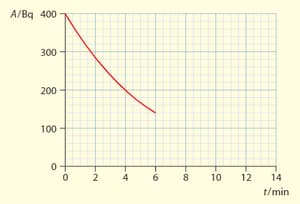
The sample contains a radioactive element that decays into a stable element . At , no atoms of are in the sample present
in the sample. Determine the time after which the ratio of atoms to atom is
In a study of the intensity of gamma rays from a radioactive source, it is suspected that the counter rate at a distance from the source behaves as where = unknown constant. A set of data for is given. Outline how the data must be plotted in order to get a straight line
The intensity of gamma rays of specific energy (monochromatic rays) decreases exponentially with the thickness of the absorbing material according to the equation
where = intensity at the face of the absorber and is a constant depending upon the material
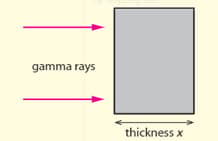
Discuss how the intensity and thickness should be plotted in order to allow an accurate determination of the constant .
State the name of dominant forces between two protons separated by a distance of
State the name of dominant forces between two protons separated by a distance of .
Large stable nuclei have more neutrons than protons. Explain this observation by reference to the properties of strong nuclear force.
