K A Tsokos Solutions for Chapter: Atomic, Nuclear and Particle Physics, Exercise 3: Test yourself
K A Tsokos Physics Solutions for Exercise - K A Tsokos Solutions for Chapter: Atomic, Nuclear and Particle Physics, Exercise 3: Test yourself
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 7: Atomic, Nuclear and Particle Physics, Exercise 3: Test yourself with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Physics for the IB Diploma 6th Edition solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from K A Tsokos Solutions for Chapter: Atomic, Nuclear and Particle Physics, Exercise 3: Test yourself with Hints & Solutions
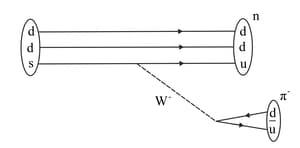
Using the basic weak interaction vertex involving W boson and two quarks or leptons given in the figure below, draw Feynman diagram to represent the following process.
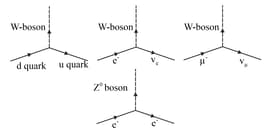
Using the basic weak interaction vertex involving W boson and two quarks or leptons given in the figure below, draw a Feynman diagram to represent the following process.
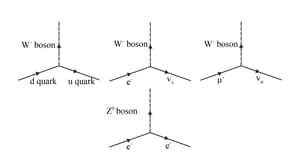
Using the basic weak interaction vertex involving W boson and two quarks or leptons given in the figure below, draw a Feynman diagram to represent the following process.
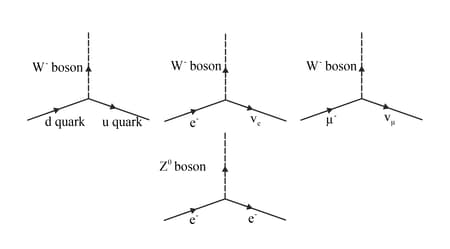
Using the basic weak interaction vertex involving W boson and two quarks or leptons given in the figure below, draw a Feynman diagram to represent the following process.
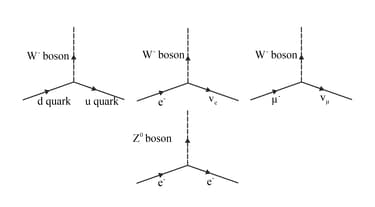
Using the basic weak interaction vertex involving a W boson and two quarks and leptons given in below figure, state three possibly ways in which the W boson can decay.
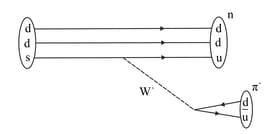
Using the basic weak interaction vertex involving a Z boson and two quarks and leptons as given in the figure. Draw a Feynman diagram to represent the following process.
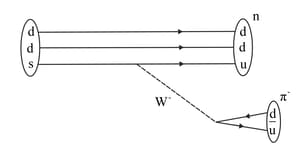
Using the basic weak interaction vertex involving a Z boson and two quarks and leptons as given in the figure. Draw a Feynman diagram to represent the following process.
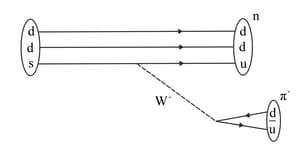
Using the basic weak interaction vertex involving a Z boson and two quarks and leptons as given in the figure. Draw a Feynman diagram to represent the following process.