K A Tsokos Solutions for Chapter: Electricity and Magnetism, Exercise 2: Test yourself
K A Tsokos Physics Solutions for Exercise - K A Tsokos Solutions for Chapter: Electricity and Magnetism, Exercise 2: Test yourself
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 5: Electricity and Magnetism, Exercise 2: Test yourself with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Physics for the IB Diploma 6th Edition solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from K A Tsokos Solutions for Chapter: Electricity and Magnetism, Exercise 2: Test yourself with Hints & Solutions
Outline the mechanism by which electric current heats up the material.
Explain why the doubling of the length of a wire at a constant temperature, will double its resistance?
The graph shows the current as a function of voltage across the same piece of metal wire which is kept at two different temperature.
Discuss whether the wire obey Ohm's law.
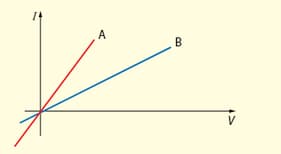
The graph shows the current as a function of the voltage across the same piece of metal wire which is kept at two different temperatures.
Suggest which of the two lines on the graph corresponds to the higher temperature.
The current in a device obeying Ohm's law is when connected to a source of potential difference of .What will be the potential difference across the same device be when a current of flows in it?
A resister obeying Ohm's law is measured to have a resistance of when a current of flows in it. Determine the resistance when the current is
The heating element of an electric kettle has a current of when connected to a source of potential difference . Calculate the resistance of the heating element.
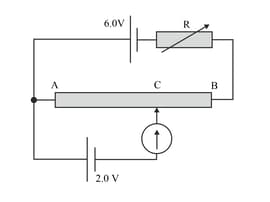
The top cell in the circuit in the diagram has emf 6.0V. The emf of the cell in the lower part of the circuit is 2.0V. Both cells have negligible internal resistance. AB is a uniform wire of length 1.0m and resistance . When the variable resistor is set at The galvanometer shows zero current. Determine the length AC.