K A Tsokos Solutions for Chapter: Thermal Physics, Exercise 2: Test yourself
K A Tsokos Physics Solutions for Exercise - K A Tsokos Solutions for Chapter: Thermal Physics, Exercise 2: Test yourself
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 3: Thermal Physics, Exercise 2: Test yourself with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Physics for the IB Diploma 6th Edition solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from K A Tsokos Solutions for Chapter: Thermal Physics, Exercise 2: Test yourself with Hints & Solutions
The point marked in the diagram represents the state of a fixed quantity of ideal gas in a container with a moveable piston. The temperature of the gas in the state shown is . Copy the diagram. Indicate on the diagram the point representing separate change.
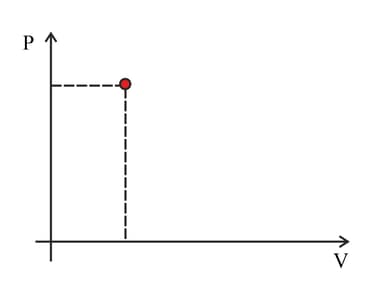
a. The volume doubles at a constant temperature.
The point marked in the diagram represents the state of a fixed quantity of ideal gas in a container with a moveable piston. The temperature of the gas in the state shown is . Copy the diagram. Indicate on the diagram the point representing separate change.
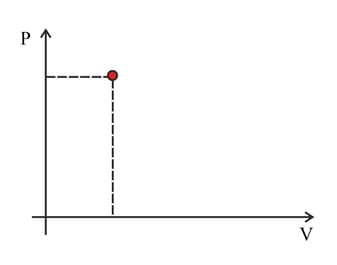
b. The volume doubles at a constant pressure.
The point marked in the diagram represents the state of a fixed quantity of ideal gas in a container with a moveable piston. The temperature of the gas in the state shown is . Copy the diagram. Indicate on the diagram the point representing separate change.
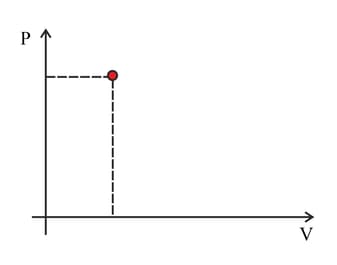
c. The pressure halved at constant volume.
Two ideal gases are kept at the same temperature in two containers separated by the valve, as shown in the diagram. 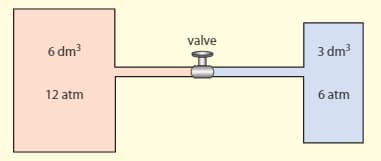
Estimate the pressure when the valve is opened. (The temperature stays the same)
The diagram shows a cylinder in vacuums, which has a movable, frictionless piston at the top. An ideal gas is kept in the cylinder. The piston is at a distance of from the bottom of the cylinder and the volume of the cylinder . The weight on the top of the cylinder has a mass of . The temperature of the gas is .
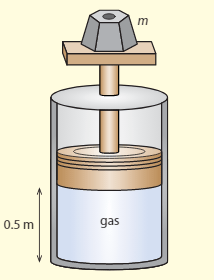
a. Calculate the pressure of the gas.
The diagram shows a cylinder in vacuums, which has a movable, frictionless piston at the top. An ideal gas is kept in the cylinder. The piston is at a distance of from the bottom of the cylinder and the volume of the cylinder . The weight on the top of the cylinder has a mass of . The temperature of the gas is .
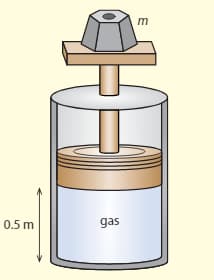
b. Determine how many molecules there are in the gas.
The diagram shows a cylinder in vacuums, which has a movable, frictionless piston at the top. An ideal gas is kept in the cylinder. The piston is at a distance of from the bottom of the cylinder and the volume of the cylinder . The weight on the top of the cylinder has a mass of . The temperature of the gas is .
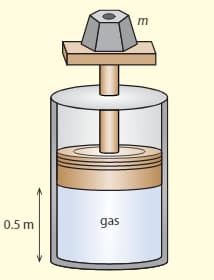
c. The temperature is increased to . Calculate the new volume of the gas.
Show that the average (r.m.s) speed of molecules of gas of molar mass kept at a temperature is given by .
