TOPICWISE QUESTIONS
K K Sharma Physics Solutions for Exercise - TOPICWISE QUESTIONS
Simple step-by-step solutions to TOPICWISE QUESTIONS questions of Mechanical Properties of Fluids from Chapterwise/Topicwise Daily Practice Problems (DPP) Mechanics II NEET. Also get 3D topic explainers, cheat sheets, and unlimited doubts solving on EMBIBE.
Questions from TOPICWISE QUESTIONS with Hints & Solutions
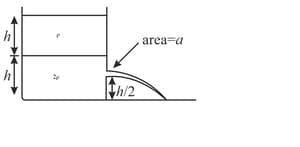
A large open tank has two holes in the wall. One is a square hole of side at a depth from the top and the other is a circular hole of radius at a depth from the top. When the tank is completely filled with water, the quantities of water flowing out per second from both the holes are same. Then, the radius is equal to,
At what speed is the velocity head of water equal to the pressure head of of ?
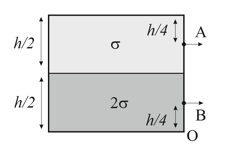
A fixed cylindrical tank having large cross-sectional area is filled with two liquids of densities and and in equal volumes as shown in the figure. A small hole of area of cross-section is made at height from the bottom. Calculate the velocity of efflux.
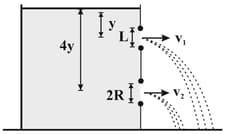
A large tank is filled with two liquids of specific gravities and . Two holes, and , are made on the wall of the tank as shown in the figure. Find the ratio of the distance from of the points on the ground where the jets from holes and strike.
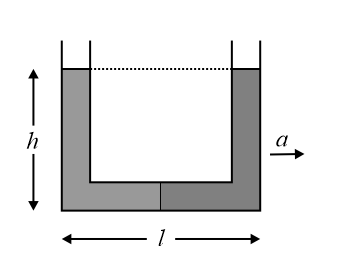
A -tube of base length filled with same volume of two liquids of densities and is moving with an acceleration on a horizontal plane as shown in the figure. If the height difference between the two surfaces (open to atmosphere) becomes zero, then the height is given by,
If the terminal speed of a sphere of gold () is in a viscous liquid, then find the terminal speed of sphere of silver () of the same size in the same liquid ().
A spherical solid ball of volume is made of a material of density . It is falling through a liquid of density . Assume that the liquid applies a viscous force on the ball that is proportional to the square of its speed , i.e.,, then the terminal speed of the ball is,
If a ball of steel attains a terminal velocity of when falling in water , then its terminal velocity in glycerine would nearly be,