Lawrie Ryan and Roger Norris Solutions for Chapter: Chemical Bonding, Exercise 19: EXAM-STYLE QUESTIONS
Lawrie Ryan Chemistry Solutions for Exercise - Lawrie Ryan and Roger Norris Solutions for Chapter: Chemical Bonding, Exercise 19: EXAM-STYLE QUESTIONS
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 4: Chemical Bonding, Exercise 19: EXAM-STYLE QUESTIONS with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Chemistry for Cambridge International AS & A Level Coursebook with Digital Access (2 Years) solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Lawrie Ryan and Roger Norris Solutions for Chapter: Chemical Bonding, Exercise 19: EXAM-STYLE QUESTIONS with Hints & Solutions
The table shows the atomic number and boiling points of some noble gases.
| Gas | helium | neon | argon | krypton | xenon |
| Atomic number | |||||
| Boiling point / |
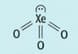
The structure of xenon trioxide is shown below.
By referring to electron pairs, explain why xenon trioxide has this shape.
The table shows the atomic number and boiling points of some noble gases.
| Gas | helium | neon | argon | krypton | xenon |
| Atomic number | |||||
| Boiling point / |
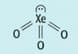
The structure of xenon trioxide is shown below.
Draw the structure of xenon trioxide to show the partial charges on the atoms and the direction of the dipole in the molecule.
Describe how sodium iodide and iodine differ in their solubility in water. Explain your answer.
Explain why molten sodium iodide is conducting electricity but molten iodine does not.
The boiling point of sodium iodide is . The boiling point of iodine is . Explain this difference.
The Pauling electronegativities of and iodine are shown. Sodium = , iodine =
Use these electronegativities values to explain why sodium iodide is an ionic compound and not a covalent compound.
Oxygen, , sulphur, , and selenium, , are in the same group in the periodic table. Explain why hydrogen selenide, , has a higher boiling point than hydrogen sulphide, .
Oxygen, , sulphur, , and selenium, , are in the same group in the periodic table. Explain why the boiling point of water is so much higher than the boiling point of hydrogen sulphide.