Lawrie Ryan and Roger Norris Solutions for Chapter: Equilibria, Exercise 14: Questions
Lawrie Ryan Chemistry Solutions for Exercise - Lawrie Ryan and Roger Norris Solutions for Chapter: Equilibria, Exercise 14: Questions
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 8: Equilibria, Exercise 14: Questions with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Chemistry for Cambridge International AS & A Level Coursebook with Digital Access (2 Years) solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Lawrie Ryan and Roger Norris Solutions for Chapter: Equilibria, Exercise 14: Questions with Hints & Solutions
Hydrazine, , is a weak base. Write a chemical equation to show the equilibrium reaction of hydrazine with water.
Hydrazine, , is a weak base. State the relative concentrations (high or low) of the , molecules and the products.
The of a solution depends on the hydrogen ion (hydroxonium ion) concentration. Which concentration of ethanoic acid in Table has the highest concentration of hydrogen ions in solution?
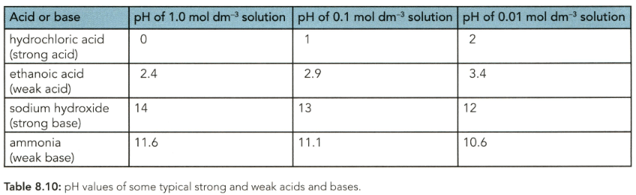
Which acid or alkali in Table has the highest concentration of hydroxide ions?

Explain why a solution of ethanoic acid has a lower electrical conductivity than a solution of hydrochloric acid.
Both hydrochloric acid and ethanoic acid react with magnesium. The rate of reaction of hydrochloric acid with magnesium is much faster than the rate of reaction of ethanoic acid. Explain why.
