Lawrie Ryan and Roger Norris Solutions for Chapter: Lattice Energy, Exercise 18: EXAM-STYLE QUESTIONS
Lawrie Ryan Chemistry Solutions for Exercise - Lawrie Ryan and Roger Norris Solutions for Chapter: Lattice Energy, Exercise 18: EXAM-STYLE QUESTIONS
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 19: Lattice Energy, Exercise 18: EXAM-STYLE QUESTIONS with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Chemistry for Cambridge International AS & A Level Coursebook with Digital Access (2 Years) solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Lawrie Ryan and Roger Norris Solutions for Chapter: Lattice Energy, Exercise 18: EXAM-STYLE QUESTIONS with Hints & Solutions
Use ideas about ion polarisation to explain why barium carbonate is more stable to thermal decomposition than magnesium carbonate.
The diagram shows the enthalpy changes when sodium chloride is dissolved in water.
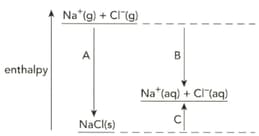
Define the term enthalpy change of solution.
The diagram shows the enthalpy changes when sodium chloride is dissolved in water.
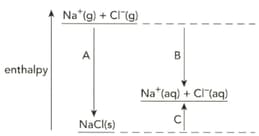
Define the term enthalpy change of hydration.
The diagram shows the enthalpy changes when sodium chloride is dissolved in water.
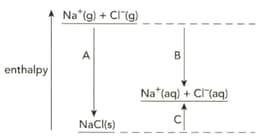
Write symbol equation that describe the enthalpy change of solution of sodium chloride.
The diagram shows the enthalpy changes when sodium chloride is dissolved in water.
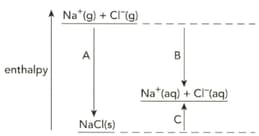
Write symbol equation that describe the enthalpy change of hydration of the chloride ion.
The diagram shows the enthalpy changes when sodium chloride is dissolved in water.
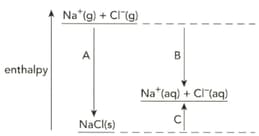
Name the enthalpy changes labelled A, B and C.
Draw the water molecules around magnesium ions and sulfate ions in a solution of magnesium sulfate.
Explain, in terms of differences of lattice energies and enthalpy changes of hydration, why magnesium sulfate is more soluble in water than calcium sulfate.
