NCERT Solutions for Chapter: Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance, Exercise 4: LA
NCERT Physics Solutions for Exercise - NCERT Solutions for Chapter: Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance, Exercise 4: LA
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 2: Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance, Exercise 4: LA with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. NCERT Exemplar Physics - Class 12 solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from NCERT Solutions for Chapter: Electrostatic Potential and Capacitance, Exercise 4: LA with Hints & Solutions
A parallel plate capacitor is filled by a dielectric whose relative permittivity varies with the applied voltage as where . A similar capacitor with no dielectric is charged to . It is then connected to the uncharged capacitor with the dielectric. Find the final voltage on the capacitors.
A capacitor is made of two circular plates of radius each, separated by a distance . The capacitor is connected to a constant voltage. A thin conducting disc of radius and thickness is placed at a centre of the bottom plate. Find the minimum voltage required to lift the disc if the mass of the disc is
In a quark model of elementary particles, a neutron is made of one up quarks [charge ] and two down quarks [charges ]. Calculate the electrostatic potential energy of the neutron and compare it with its mass Repeat the above exercise for a proton which is made of two up and one down quark.
Two metal spheres, one of radius and the other of radius , both have same surface charge density . They are brought in contact and separated. What will be the new surface charge densities on them?
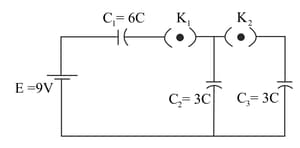
In the circuit shown in Figure initially is closed and is open. What are the charges on each capacitors. Then was opened and was closed (order is important), What will be the charge on each capacitor now?
Calculate potential on the axis of a disc of radius due to a charge , uniformly distributed on its surface.
Two charges and are placed at and respectively. Find locus of points where the potential a zero.
Two charges each are separated by distance . A third charge is kept at mid point . Find potential energy of as a function of small distance from due to charges. Sketch P.E. and convince yourself that the charge at is in an unstable equilibrium.
