Kirchhoff's Laws
Important Questions on Kirchhoff's Laws
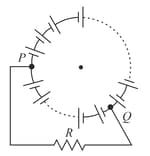
For the potentiometer circuit, shown in Fig. , points and represent the two terminals of an unknown emf E. A student observed that when the jockey is moved from the end to the end of the potentiometer wire, the deflection in the galvanometer remains in the same direction. What are the two possible faults in the circuit that could result in this observation?
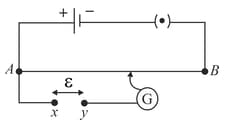
If the galvanometer deflection at the end is
(i) more (ii) less
than that at the end , which of the two faults, listed above, would be there in the circuit? Give reasons in support of your answer in each case.
In the potentiometer circuit shown in Fig. , the balance (null) point is at X. State with reason, where the balance point will be shifted when
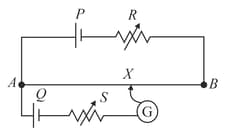
Cell is replaced by another cell whose emf is lower than that of cell
In the potentiometer circuit shown in Fig. , the balance (null) point is at X. State with reason, where the balance point will be shifted when
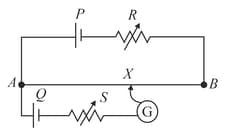
Resistance is increased, keeping constant.
In the potentiometer circuit shown in Fig. , the balance (null) point is at X. State with reason, where the balance point will be shifted when
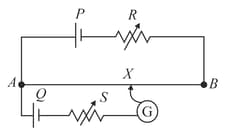
Resistance is increased, keeping all parameters unchanged.
In the circuit shown in Fig. , find the current through the resistor.
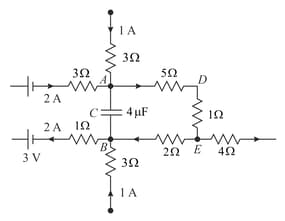
Problem 40. A part of the circuit in a steady state along with the currents flowing in the branches, the values of resistance, etc. is shown in Fig. Calculate the energy stored in the capacitor.
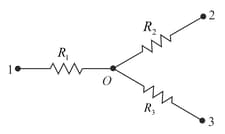
Find the current flowing through the resistance of the circuit shown in Fig. . Given and and the potentials of points 1,2 and 3 are and .
cells, each of emf and internal resistance are connected in a closed circuit so that the positive terminal of a cell is joined to the negative terminal of the next, as shown in Fig. . Any two points of the circuit are connected by an external resistance . Find the current in
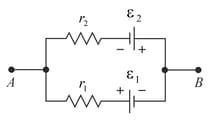
Find the and internal resistance of a battery which is equivalent to a parallel combination of two batteries of emfs and and internal resistances and respectively, with polarities as shown in Fig.
 .
.
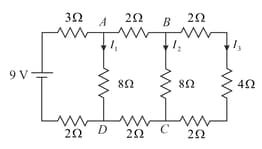
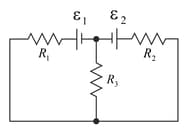
Determine the currents through the resistors and shown in Fig.
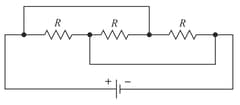
Three equal resistors, each of ohm, are connected as shown in Fig. . A battery of volt and of internal resistance is connected across the circuit. Calculate the value of for which the heat generated in the circuit is maximum.
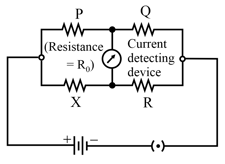
Describe briefly the device, based on the above condition. Draw a circuit diagram for this device and discuss, in brief, how it is used for finding an unknown resistance.
Obtain the condition under which the current flowing, in the 'current detecting device', used in the circuit shown in the figure, becomes zero.
What does the term 'end error' in a metre bridge circuit metre and how is it corrected ? How will be balancing point be affected, if the positions of the battery and galvanometer are inter- changed in a metre bridge experiment ? Give reason for your answer.
Why is the use of a potentiometer preferred over that of a voltmeter for the measurement of emf of a cell ?
You are required to find the internal resistance of a primary cell in the laboratory. Draw a circuit diagram of the apparatus you will use to determine it. Explain the principle of the experiment. Give the formula used.
Name the device used for measuring the emf of a cell.
On what conservation principle is the Kirchhoff's second law based?
On what conservation principle is the Kirchoff's first law based ?
Can Kirchhoff's laws be applied to both d.c. and a.c. circuits ?

