B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Sound Waves and Doppler Effect, Exercise 3: Exercises
B M Sharma Physics Solutions for Exercise - B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Sound Waves and Doppler Effect, Exercise 3: Exercises
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 8: Sound Waves and Doppler Effect, Exercise 3: Exercises with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. PHYSICS FOR JOINT ENTRANCE EXAMINATION WAVES AND THERMODYNAMICS solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Sound Waves and Doppler Effect, Exercise 3: Exercises with Hints & Solutions
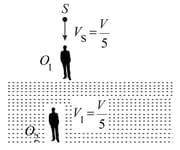
In the figure shown an observer floats (static) on water surface with ears in air while another observer is moving upwards with constant velocity in water. The source moves down with constant velocity and emits sound of frequency The velocity of sound in air is and that in water is . For the situation shown in figure.
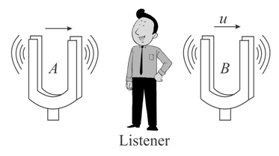
Two tuning forks and are vibrating at the same frequency . A listener is standing midway between the forks. If both tuning forks move to the right with a velocity of , find the number of beats heard per second by the Tistener (speed of sound in air is ).
A driver in a stationary car horns which produces monochromatic sound waves of frequency , normally towards a reflecting wall. If the wall approaches the car with a velocity , calculate the frequency of sound reflected from wall and heard by the driver. What is the percentage change of sound frequency on reflection from the wall?
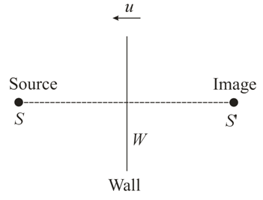
A source of sound of frequency is moving towards a wall with a velocity of . How many beats per second will be heard by an observer standing in such a position that the source is between and wall?
A vibrating tuning fork tied to the end of a string long is whirled round a circle. If it makes two revolutions in a second, calculate the ratio of the frequencies of the highest and the lowest notes heard by an observer situated in the plane of the tuning fork. Velocity of sound is .
A source of sonic oscillations with frequency and a receiver are located on the same normal to a wall. Both the source and receiver are stationary, and the wall recedes from the source with velocity . Find the beat frequency (in ) registered by the receiver. The velocity of sound is .
A locomotive approaching a crossing at a speed of sounds a whistle of frequency when from the crossing. There is no wind, and the speed of sound in air is. What frequency is heard by an observer from the crossing on the straight road which crosses the railroad at right angles?
A whistle of frequency is dropped from a height above the ground. At the same time, a detector is projected upwards with velocity along the same line. If the velocity of sound is , find the frequency (in ) detected by the detector after
