B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Newton's Laws of Motion (Without Friction), Exercise 72: Exercises
B M Sharma Physics Solutions for Exercise - B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Newton's Laws of Motion (Without Friction), Exercise 72: Exercises
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 6: Newton's Laws of Motion (Without Friction), Exercise 72: Exercises with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. PHYSICS For Joint Entrance Examination JEE (Advanced) Mechanics I solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Newton's Laws of Motion (Without Friction), Exercise 72: Exercises with Hints & Solutions
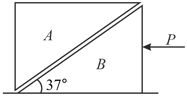
A small block of mass is kept at rest at the bottom of the inclined plane of a wedge of mass . A force of is applied on the wedge horizontally as shown in the diagram. All the surfaces are smooth. Determine the time taken in seconds by the mass to reach the highest point of the inclined plane of the wedge?
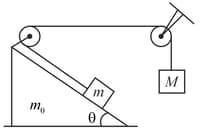
In the system shown in figure, all surfaces are smooth and string and pulleys are light. Angle of wedge . When released from rest, it was found that the wedge of mass does not move. Find .
In the system shown in figure, the two springs and have force constant each. Pulley, springs and strings are all massless. Initially, the system is in equilibrium with spring stretched and relaxed. The end of the string is pulled down slowly through a distance . By what distance (in ) does the block of mass move?
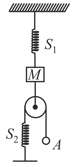
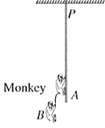
A monkey is climbing up a rope tied to a rigid support. The monkey is holding on the tail of monkey . If the tail can tolerate a maximum tension of , what maximum force should monkey apply on the rope in order to carry monkey with it?
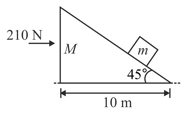
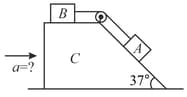
The upper surface of block is horizontal and its right part is inclined to the horizontal at angle . The mass of blocks and are and , respectively. Neglect friction and mass of the pulley. Calculate acceleration with which block should be moved to the right so that and can remain stationary relative to it.
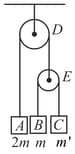
In the arrangement shown in figure, pulley and are small and frictionless. They do not rotate but threads slip over them without friction and their masses being and respectively, while masses of block and are and , respectively. When the system is released from rest, downward accelerations of blocks and relative to are found to be and , respectively.
Find the ratio of the acceleration of blocks and , relative to the ground.
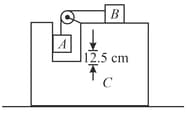
A small light pulley is attached with a block of mass as shown in the figure. Block of mass is placed on the top horizontal surface of . Another block of mass is hanging from a string attached with and passing over the pulley. Taking and neglecting friction, find the acceleration of block (in ) when the system is released from rest.
Blocks and each have same mass . Determine the largest horizontal force (in newton) which can be applied to so that will not slip up on . Neglect any friction.