B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Electric Potential, Exercise 6: Exercise
B M Sharma Physics Solutions for Exercise - B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Electric Potential, Exercise 6: Exercise
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 3: Electric Potential, Exercise 6: Exercise with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. PHYSICS for Joint Entrance Examination JEE (Advanced) Electrostatics and Current Electricity solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from B M Sharma Solutions for Chapter: Electric Potential, Exercise 6: Exercise with Hints & Solutions
Two small spheres are attached to the ends of a long light nonconducting rod at a distance from each other. A third, middle sphere can slide along the rod without friction as shown. All three spheres are nonconducting, have identical masses and a positive charge is distributed evenly on the surface of each sphere. The whole system is placed on a horizontal frictionless nonconducting surface. Initially, all three spheres are at rest and the middle sphere is located a distance from one of the ends of the rod and a distance from the other. Find the maximum speed (in ) of the middle sphere after the system is released.
Three-point charges of each are placed at the corners of an equilateral triangle with side If this system is supplied energy at the rate of how much time (in hour) will be required to move one of the charges to the midpoint of the line joining the other two?
A radioactive source in the form of a metal sphere of radius emits beta particles (electrons) at the rate of particles per second. The source is electrically insulated. How long will it take (in ) for its potential to be raised by assuming that of the emitted beta particles escape from the source?
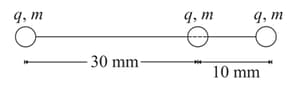
The figure shows four situations in which charges as indicated are fixed on an axis. How many situations is there a point to the left of the charges where an electron would be in equilibrium?
An electric field is given by . Find the work done (in ) in moving a charge from to
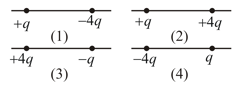
The arrangement is shown consists of three elements.
a. A thin rod of charge that forms a full circle of radius
b. A second thin rod of charge that forms a circular arc of radius and concentric with the full circle, subtending an angle of at the centre of the full circle.
c. An electric dipole with a dipole moment that is perpendicular to a radial line and has magnitude
Find the net electric potential in volts at the centre.
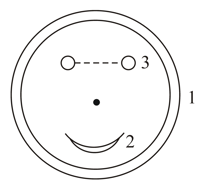
An infinite plane of charge with is tilted at a angle to the vertical direction as shown below. Find the potential difference, in volts, between points and at distance apart (where is vertically above ).
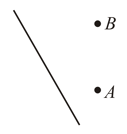
A small sphere of mass carrying a positive charge is connected with a light, flexible and inextensible string of length and whirled in a vertical circle. If a vertically upward electric field of strength exists in the space, calculate minimum velocity of sphere (in ) required at highest point so that it may just complete the circle.
