Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter, Exercise 1: Exercise
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter, Exercise 1: Exercise
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 11: Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter, Exercise 1: Exercise with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Physics Crash Course (Based on Revised Syllabus-2023) solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Dual Nature of Radiation and Matter, Exercise 1: Exercise with Hints & Solutions
State the objective of Davisson and Germer experiment.
First order diffraction is observed in Davisson and Germer experiment. Accelerating voltage in volt. If the distance between reflecting surfaces of the used crystal is , find out the angle of diffraction.
State importance of Davisson and Germer experiment.
Describe the Davisson and Germer experiment.
The following graph shows the variation of stopping potential with frequency of the incident radiation for two photosensitive metals and :
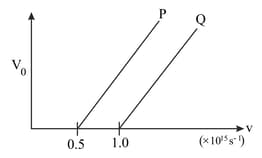
Which metal,
(i) has smaller threshold wavelength.
(ii) has smaller kinetic energy.
What is photo-electric effect?
For a certain metal threshold wavelength is . Calculate the work function of the metal.
When a metallic surface is illuminated with light of frequency the maximum kinetic energy of emitted electrons is . When the same surface is illuminated by light of frequency the maximum kinetic energy of emitted electrons is . Find out work function of the metal.
