Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Thermodynamics, Exercise 1: Level 1
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Thermodynamics, Exercise 1: Level 1
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 10: Thermodynamics, Exercise 1: Level 1 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Physics Crash Course JEE Main solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Thermodynamics, Exercise 1: Level 1 with Hints & Solutions
A system is taken from state to state via two different paths.
Path with and
Path
Find the value of (in ) for the second path.
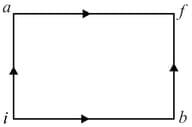
Consider to be the universal gas constant. Given that, the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of of an ideal monatomic gas from to when no work is done is . Then is
A given quantity of gas is taken from the state to the state reversibly by two paths, directly and as shown in the figure below:
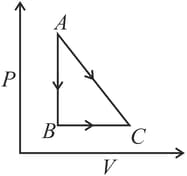
During the process , work done by the gas is and heat absorbed is . If during the process , the work done by the gas is , the heat absorbed is
of is contained in a cubical container of side and maintained at a temperature of . The isothermal bulk modulus of elasticity of the gas in terms of universal gas constant is . Find the value of .
A gas with the ratio of specific heat expands from an initial pressure of and volume to pressure and volume adiabatically. The work done is given by
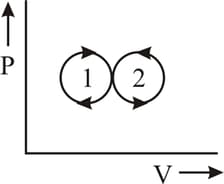
The net amount of the work done in the following indicator diagram is -
A heat engine operating between degrees and degrees has an efficiency of that of a Carnot engine operating between the same temperatures. If the engine absorbs heat at a rate of , at what rate does it exhaust heat (in )? (Approximate the answer to the nearest integer.)
An ideal heat engine exhausting heat at is to have a efficiency. Find the temperature at which it must take heat.
