Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Kinetic Theory of Gases and Radiation, Exercise 1: Exercise 1
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Kinetic Theory of Gases and Radiation, Exercise 1: Exercise 1
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 12: Kinetic Theory of Gases and Radiation, Exercise 1: Exercise 1 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Physics Crash Course MHT-CET solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Kinetic Theory of Gases and Radiation, Exercise 1: Exercise 1 with Hints & Solutions
Assertion: The root mean square velocity of molecules of a gas having Maxwellian distribution of velocities is higher than their most probable velocity at any temperature.
Reason: A very small number of molecules of a gas possessing very large velocities increases the root mean square velocity without affecting the most probable velocity.
An ideal gas is enclosed in a cylinder at pressure of and temperature, . Then mean time between two successive collisions is . If the pressure is doubled and temperature is increased to , the mean time between two successive collisions will be close to
According to Kirchhoff's law-
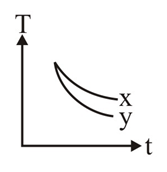
The temperature of bodies and vary with time as shown in the figure. If emissivity of bodies and are and and absorptive powers are and , (assume other conditions are identical for both), then
Assertion: Absorptive power is a dimensionless quantity and a body having low emissive power should have low absorptive power.
Reason: The ratio of emissive power to absorptive power is same for all bodies at a given temperature and is equal to the emissive power of a black body at that temperature.
If the absorption coefficient and reflection coefficient of a surface of a body are and respectively then
Assertion: A body that is a good radiator is also a good absorber of radiation at a given wavelength.
Reason: According to Kirchhoff's law the absorptivity of a body is equal to its emissivity at a given wavelength.
Which of the following is extensive variable?
