Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Wave Theory of Light, Exercise 1: Exercise 1
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Wave Theory of Light, Exercise 1: Exercise 1
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 20: Wave Theory of Light, Exercise 1: Exercise 1 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Physics Crash Course MHT-CET solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Wave Theory of Light, Exercise 1: Exercise 1 with Hints & Solutions
A plane wavefront of wavelength falls on a slit wide. A convex lens of focal length placed behind the slit focuses the light on a screen. What is the linear diameter of second maximum?
Huygens' principle of secondary wavelets may be used to
The meaning of wavefront is:-
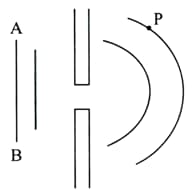
A monochromatic plane wave is diffracted at a small aperture. The diagram illustrates successive wavefronts. The time after which some portion of the wavefront will reach $\mathrm{P}$ is $[$ Speed $=\mathrm{c}$ and wavelength $=\lambda]$
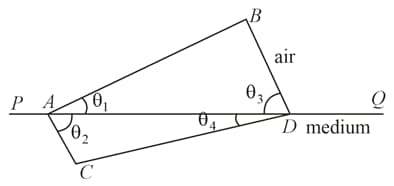
The following figure represents a wave front which passes from air to another transparent medium and produces a new wave front after refraction. The refractive index of the medium is ( is the boundary between air and the medium).
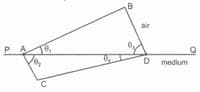
The following figure represents a wave front which passes from air to another transparent medium and produces a new wave front after refraction. The refractive index of the medium is ( is the boundary between air and the medium).
A galaxy moves with respect to the earth so that Sodium line of is observed at The speed of the galaxy is
In context of Doppler's effect in light, the term 'red shift' signifies
