Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents, Exercise 3: Level 3
Embibe Experts Physics Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents, Exercise 3: Level 3
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 15: Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents, Exercise 3: Level 3 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Physics Crash Course NEET solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Electromagnetic Induction and Alternating Currents, Exercise 3: Level 3 with Hints & Solutions
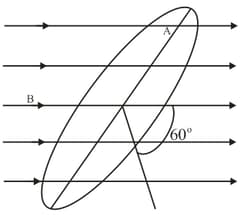
The figure represents an area situated in a uniform magnetic field and making an angle of with respect to the magnetic field. The value of the magnetic flux through the area would be equal to
Which of the following remain constant in a transformer ?
A sinusoidal voltage with a frequency of is applied to a series circuit with a resistance of , inductance of and a capacitance of . The magnitude of impedance of the circuit is close to
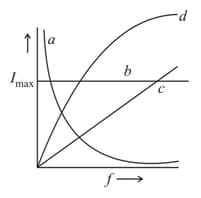
Three identical emf sources are attached to a single circuit element: a resistor, a capacitor, or an inductor. The current amplitude is then measured as a function of frequency. Which one of the following curve corresponds to inductive circuit?
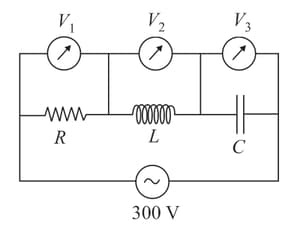
The figure shows an LCR network connected to a supply. The circuit elements are such that Three voltmeters and are connected as shown. Which of the following represents the correct set of readings of the voltmeters?
A metallic square loop is moving in its own plane with velocity in a uniform magnetic field perpendicular to its plane as shown in the figure. An electric field is induced
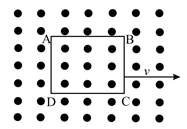
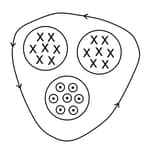
Figure shows three regions of magnetic field each of area and in each region magnitude of magnetic field decreases at a constant rate . If is induced electric field, then value of line integral along the given loop is equal to,
In a – growth circuit, inductance and resistance used are and , respectively. If at , current in the circuit is , then applied direct current is,
