Centre of Mass Frame of Reference or Centroidal Frame
Important Questions on Centre of Mass Frame of Reference or Centroidal Frame
Two identical particles and of mass each are connected together by a light and inextensible string of length The particle are held at rest in air in same horizontal level at a separation Both particles are released simultaneously and one of them (say ) is given speed vertically upward. The maximum height attained by the centre of mass of the system of and from initial level is (Ignore air resistance).
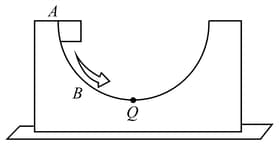
Block is released on the circular track of bigger block from rest from the position as shown in figure. Friction is absent everywhere. Choose the correct statement.
A trolley is moving horizontally with a velocity of w.r.t. earth. A man starts running in the direction of motion of trolley from one end of the trolley with a velocity w.r.t. the trolley. After reaching the opposite end, the man turns back and continues running with a velocity of w.r.t. trolley in the backward direction. If the length of the trolley is then the displacement of the man with respect to earth, measured as a function of time, will attain a maximum value of
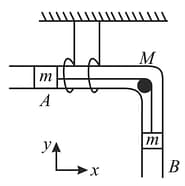
In figure, a hollow tube of mass is free in horizontal direction. The system is released from rest. There is no friction present. The tube and blocks are taken as system.
i. Momentum of the system is conserved in -direction.
ii. Speed of w.r.t. Speed of w.r.t.
¡ii. Trajectory of centre of mass is -constant. iv. Centre of mass has finite acceleration.
Evaluate the above statements and choose the correct option from the following:
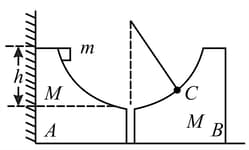
Two identical blocks, having mass each, are conjugated and placed on a smooth floor as shown in figure. A small block of mass is released from position as shown. Velocity of block is maximum
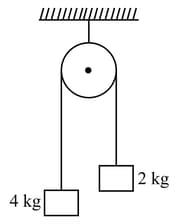
For the system shown in figure, the string is light and pulley is frictionless. The block is given an upward velocity of The centre of mass of the two blocks
will [neglect the impulse duration]
An object of mass is launched from the ground at at an angle of above the horizontal with a speed of At some time after its launch, an explosion splits the projectile into two pieces. One piece of mass is observed at at Find the location of second piece at
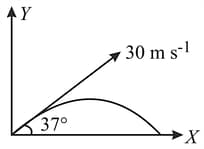
In a system of particles mass is subjected to a force of along ve -axis and another mass is subjected to a force of along ve -axis. The magnitude of acceleration of centre of mass and the angle made by it with -axis are given, respectively, by
Two blocks of masses and are placed on a frictionless surface and connected by a spring. An external kick gives a velocity of to the heavier block in the direction of lighter one. The magnitudes of velocities of two blocks in the centre of mass frame after the kick are, respectively,
Two particles are shown in figure At a constant force starts acting on the man. Find the velocity of the centre of mass of these particles at
A cracker is thrown into air with a velocity of at an angle of with the vertical. When it is at a height of from the ground, it explodes into a number of pieces which follow different parabolic paths. What is the velocity of centre of mass, when it is at a height of from the ground?
A man of mass is standing on a plank of mass kept on a rough surface. When the man walks from left to right on the plank, the centre of mass (man + plank) of the system:
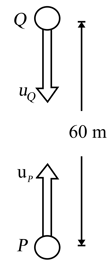
Two particles and have mass and respectively. They are projected along a vertical line with velocity and when separation between them was was projected vertically up while was projected vertically down. Calculate the maximum height attained (in ) by the centre of mass of the system of two particles, measured from the initial position of Assume that the particles do not collide and that the ground is far below their point of projection
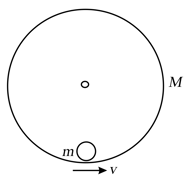
A ring of mass and radius is kept on a frictionless horizontal surface such that its plane is parallel to horizontal plane. A particle of mass is placed in contact with the inner surface of ring as shown figure. An initial velocity is given to the particle along the tangent of the ring. Find the magnitude of the force of interaction (in milli-newton) between the particle and ring.
Two masses ' ' and ' ' having mass and respectively are kept on a smooth horizontal table as shown in the figure. The mass ' ' is given a velocity perpendicular to the string parallel to the table. If and then find the tension in the string (in ).
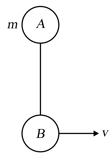
A ladder of mass is handing from ceiling as shown in figure. Three men and C of masses and are climbing the ladder. Man A is climbing with upward retardation is climbing up with a constant speed of and is climbing with upward acceleration of Find the tension in the string supporting the ladder (in ).
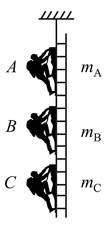
A child of mass jumps from cart to cart and then immediately back to cart The mass of each cart is and they are initially at rest. In both the cases the child jumps at relative to the cart. If the cart moves along the same line with negligible friction with the final velocities of and respectively, then the ratio of and is . Write the value of .
A ball of mass is allowed to roll down the wedge of mass as shown in the figure. What is the displacement of wedge (in ) when the ball reaches from to ? Take

A man of mass walks from end to the other end of a plank of mass and length placed on a smooth horizontal surface. The coefficient of friction between man and plank is as no external force in horizontal direction.
Two particles of masses and move with accelerations and respectively:

