K A Tsokos Solutions for Chapter: Circular Motion and Gravitation, Exercise 3: Exam-style questions
K A Tsokos Physics Solutions for Exercise - K A Tsokos Solutions for Chapter: Circular Motion and Gravitation, Exercise 3: Exam-style questions
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 6: Circular Motion and Gravitation, Exercise 3: Exam-style questions with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Physics for the IB Diploma 6th Edition solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from K A Tsokos Solutions for Chapter: Circular Motion and Gravitation, Exercise 3: Exam-style questions with Hints & Solutions
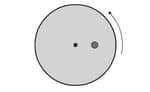
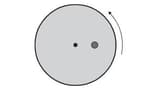
A horizontal disc of radius rotates about a vertical axis through its center. The disc makes one full revolution in .A particle of mass is placed at a distance from the centre of the disc. The particle does not move relative to the disc. The particle is to maintain the original distance from the center of the disc.Determine the maximum angular velocity (in radian per second) of the disc so that the particle does not move relative to the disc.The coefficient of static friction is .
A horizontal disc of radius rotates about a vertical axis through its center. The disc makes one full revolution in .A particle of mass is placed at a distance from the centre of the disc. The particle does not move relative to the disc. The particle is to maintain the original distance from the center of the disc. If the disc rotates with a angular velocity greater than the maximum angular velocity, qualitatively what happens to the particle?
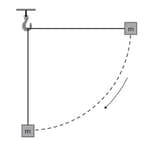
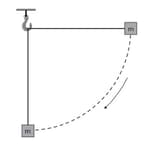
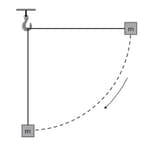
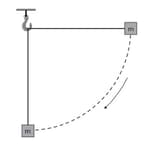
A block of mass is attached to a string of length which is initially horizontal. The mass is then released from a height that is equal to the length of string and it swings as a pendulum. The diagram shows the mass falling to the position where the string is in the vertical position.
Calculate the speed (in meter per second square) of the block when the string is in a vertical position.
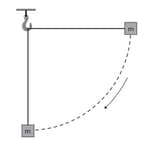
A block of mass is attached to a string of length which is initially horizontal. The mass is then released and it swings as a pendulum. The diagram shows the mass falling to the position where the string is in the vertical position.
Speed of the block when the object is in vertical position is Deduce the acceleration of the block (in meter per second square).
A block of mass is attached to a string of length which is initially horizontal. The mass is then released and swings as a pendulum. The diagram shows the mass falling to the position where the string is in the vertical position.
On a copy of the diagram, draw arrows to show the forces on the block
A block of mass is attached to a string of length which is initially horizontal. The mass is then released and swings as a pendulum. The diagram shows the mass falling to the position where the string is in the vertical position.
For when the string is in vertical position state and explain whether the block is in equilibrium.
A block of mass is attached to a string of length which is initially horizontal. The mass is then released and swings as a pendulum. The diagram shows the mass falling to the position where the string is in the vertical position,the velocity of the block in the vertical position is .
Calculate the tension in the string.
Consider two spherical bodies of mass and as in the diagram.
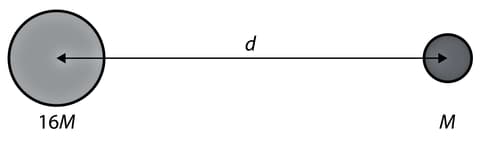
There is a point somewhere on the line joining the masses where the gravitational field strength is zero.
Draw a graph to show the variation of the gravitational field strength due to the two masses with the distance from the centre of the larger mass.