Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: States of Matter: Gaseous and Liquid states, Exercise 1: Exercise 1
Embibe Experts Chemistry Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: States of Matter: Gaseous and Liquid states, Exercise 1: Exercise 1
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 5: States of Matter: Gaseous and Liquid states, Exercise 1: Exercise 1 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Chemistry Crash Course MHT-CET solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: States of Matter: Gaseous and Liquid states, Exercise 1: Exercise 1 with Hints & Solutions
For an ideal gas, Boyle's law is best described by -
Find the density of with respect to .
Two balloons, and , containing mole and mole of helium at room temperature and ., respectively, are connected. When an equilibrium is established, the final pressure of in the system is:
The density of acetic acid vapor at and is . The number of acetic acid molecules in the cluster that is formed in the gas phase is the closest to
moles of a mixture of hydrogen and oxygen gases at a pressure of at constant volume and temperature, react to form of liquid water. The pressure of the resulting mixture will be closest to:
At , assuming ideal behaviour, the average kinetic energy of a deuterium molecule is:
In the following compressibility factor vs. pressure graph at , the compressibility of at pressures deviates from ideal behaviour because:
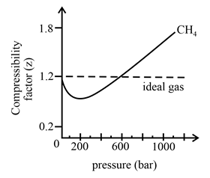
One mole, each of the two gases and , are stored separately in two cylinders at at pressures and , respectively. The difference in the compressibilities of the two gases, , is:
