Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Chemical Kinetics, Exercise 1: Exercise 1
Embibe Experts Chemistry Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Chemical Kinetics, Exercise 1: Exercise 1
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 17: Chemical Kinetics, Exercise 1: Exercise 1 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Chemistry Crash Course KCET (UG) solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Chemical Kinetics, Exercise 1: Exercise 1 with Hints & Solutions
A catalyst increases the rate of reaction by:
In the Lindemann theory of unimolecular reactions, it is shown that the apparent rate constant for such a reaction is, , where is the concentration of the reactant and is a constant. Calculate the value of for which has of its limiting value, at tending to infinitely large values. Given, .
Thermal decomposition of occurs as per the equation below:
.
The correct statement is:
For an elementary reaction of reversible nature, net rate is: , hence, given reaction is:
The decay profiles of three radioactive species and are given below:
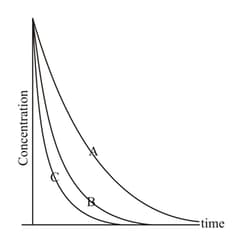
These profiles imply that the decay constants and follow the order:
Consider the following reversible first-order reaction of at an initial concentration . The values of the rate constants are and .
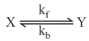
A plot of concentration of and as function of time is:
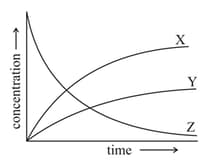
Consider the reaction : . In the figure below, identify the curves and associated with the three species in the reaction.
For an elementary reaction, the net rate is . Thus, select the correct statement:
