Resnick & Halliday Solutions for Chapter: Images, Exercise 1: Problems
Resnick & Halliday Physics Solutions for Exercise - Resnick & Halliday Solutions for Chapter: Images, Exercise 1: Problems
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 34: Images, Exercise 1: Problems with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Principles Of Physics International Student Version solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Resnick & Halliday Solutions for Chapter: Images, Exercise 1: Problems with Hints & Solutions
In the given spherical mirrors, object stands on the central axis of a spherical mirror. For this situation, each problem in the table below gives object distance (), the type of mirror and then, the distance (, without proper sign) between the focal point and the mirror. Find the radius of curvature (including sign), the image distance and the lateral magnification Also, determine whether the image is real or virtual , inverted from object or non-inverted and on the same side of the mirror as or on the opposite side.
Object stands on the central axis of a thin symmetric lens. For this situation, each problem in table refers to the lens type, converging or diverging the focal distance the object distance the image distance and the lateral magnification (All distances are in ) It also refers to whether the image is real or virtual inverted or non-inverted from and on the same side of the lens as or on the opposite side. Fill in the missing information, including the value of when only inequality is given. Where only a sign is missing, answer with the sign.
Spherical refracting surfaces are given. An object stands on the central axis of a spherical refracting surface. For this situation, each problem in Table refers to the index of refraction where the object is located, the index of refraction on the other side of the refracting surface, the object distance the radius of curvature of the surface, and the image distance (All distances are in ) Fill in the missing information, including whether the image is real or virtual and on the same side of the surface as object or on the opposite side.
Two-lens systems. In the figure, stick figure (the object) stands on the common central axis of two thin, symmetric lenses, which are mounted in the boxed regions. Lens is mounted within the boxed region closer to which is at object distance Lens is mounted within the farther boxed region, at distance . Each problem in Table refers to a different combination of lenses and different values for distances, which are given in . The type of lens is indicated by for converging and for diverging; the number after or is the distance between a lens and either of its focal points (the proper sign of the focal distance is not indicated).
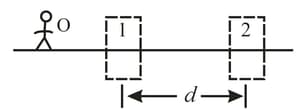
Find the image distance for the image produced by lens (the final image produced by the system) and the overall lateral magnification for the system, including signs. Also, determine whether the final image is real or virtual , inverted from object or non-inverted , and on the same side of lens as the object or on the opposite side.
Lenses with given radii. Object stands in front of a thin lens, on the central axis. For this situation, each problem in the table gives object distance index of refraction of the lens, radius of the nearer lens surface, and radius of the farther lens surface. (All distances are in centimetres.) Find (a) the image distance and (b) the lateral magnification of the object, including signs. Also, determine whether the image is (c) real () or virtual (), (d) inverted (I) from object or noninverted (), and (e) on the same side of the lens as object or on the opposite side.
Thin lenses Object stands on the central axis of a thin symmetric lens. For this situation, each problem in the table gives object distance (centimetres), the type of lens () stands for converging and () for diverging, and then the distance (centimetres, without proper sign) between a focal point and the lens. Find (a) the image distance and (b) the lateral magnification of the object, including signs. Also, determine whether the image is (c) real () or virtual (), (d) inverted from object or noninverted and (e) on the same side of the lens as object or on the opposite side.
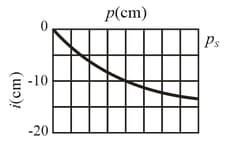
An object is placed against the center of a thin lens and then moved from it along the central axis as the image distance is measured. The figure gives versus object distance out to What is the image distance when
A concave shaving mirror has a radius of curvature of It is positioned so that the (upright) image of a man's face is times the size of the face. How far is the mirror from the face?
