Priyanka B Solutions for Chapter: The Human Eye and Colourful World, Exercise 2: Assignment-2
Priyanka B Physics Solutions for Exercise - Priyanka B Solutions for Chapter: The Human Eye and Colourful World, Exercise 2: Assignment-2
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 2: The Human Eye and Colourful World, Exercise 2: Assignment-2 with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. ESSENTIALS OF PHYSICS CLASS X solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Priyanka B Solutions for Chapter: The Human Eye and Colourful World, Exercise 2: Assignment-2 with Hints & Solutions
State the reason for the following observation recorded from the surface of the moon.
Rainbow is never formed.
A beam of white light falling on a glass prism gets split into seven colours. A student makes the statement.
Which two positions correspond to the colour of solutions of copper sulphate and signal used to move the vehicle?
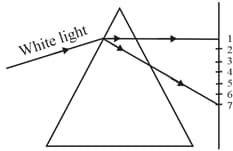
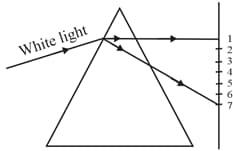
A beam of white light falling on a glass prism gets split into seven colours. A student makes the statement. Light of colour of chilly powder bends the most while the light of the colour of brinjal bends the least. Is the statement correct? Justify.
Draw a ray diagram to show the path of light ray that enters the glass obliquely. Label on it the angle of incidence and angle of derivation.
What is atmospheric refraction? Use this phenomenon to explain the following natural events :
(ii) Advanced sunrise and delayed sunset.
Draw diagrams to illustrate your answer.
What is dispersion of white light? What is the cause of such dispersion? Draw a diagram to shown the dispersion of white light by a glass prism.
A glass prism is able to produce a spectrum when white light passes through it but a glass slab does not produce any spectrum. Explain why is it so?
State the cause of dispersion of white light passing through a glass prism. How did Newton show that white light of sun contains seven colours using identical glass prisms? Draw a ray diagram to show the path of light when two identical glass prisms are arranged together in inverted positions with respect to each other and a narrow beam of white light is allowed to fall obliquely on one of the refractive surfaces of the first prism.
