R P Goyal and S P Tripathi Solutions for Chapter: Refraction of Light at Plane Surfaces, Exercise 1: EXERCISE-4(A)
R P Goyal Physics Solutions for Exercise - R P Goyal and S P Tripathi Solutions for Chapter: Refraction of Light at Plane Surfaces, Exercise 1: EXERCISE-4(A)
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 4: Refraction of Light at Plane Surfaces, Exercise 1: EXERCISE-4(A) with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Selina Icse Concise Physics For Class 10 solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from R P Goyal and S P Tripathi Solutions for Chapter: Refraction of Light at Plane Surfaces, Exercise 1: EXERCISE-4(A) with Hints & Solutions
A ray of light strikes the surface of a rectangular glass block such that the angle of incidence in air is given as . Draw a diagram to show the path chosen by the ray as it passes through the rectangular glass block and emerges from it.
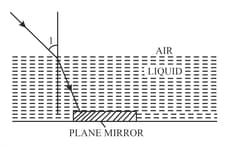
A ray of monochromatic green light enters a liquid from air, as shown in the given figure below. The angle is and angle is . Find the refractive index of liquid.
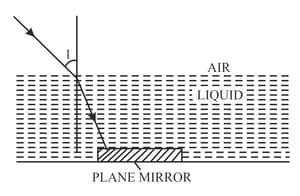
A ray of monochromatic green light enters a liquid from air, as shown in the given figure below. The angle is and angle is. Redraw the diagram if plane mirror becomes normal to the refracted ray inside the liquid. State the principle used.
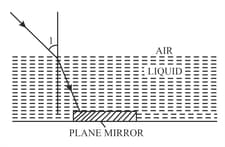
Light of a single colour is passed through a liquid having a piece of glass suspended in it. On changing the temperature of liquid, at a particular temperature the glass piece is not seen. When is the glass piece not seen?
Light of a single colour is passed through a liquid having a piece of glass suspended in it. On changing the temperature of liquid, at a particular temperature the glass piece is not seen. Why is the light of a single colour used?
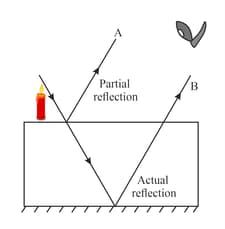
When a lighted candle is held in front of a thick plane glass mirror, various images can be seen, but the second image formed is the brightest, give reason.
When light travels from a rarer to a denser medium, its speed _____.
A ray of monochromatic green light enters a liquid from air, as shown in the given figure below. The angle is and angle is °. Show in the diagram the path of the ray after it strikes the mirror and re-enters in air. Mark in the diagram the angles where ever necessary.