R P Manchanda, Dr. Neha Jindal and, Ms. Archita Baruah Bhattacharyya Solutions for Chapter: Gravitation, Exercise 1: ASSESS YOURSELF
R P Manchanda Science Solutions for Exercise - R P Manchanda, Dr. Neha Jindal and, Ms. Archita Baruah Bhattacharyya Solutions for Chapter: Gravitation, Exercise 1: ASSESS YOURSELF
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 10: Gravitation, Exercise 1: ASSESS YOURSELF with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Together with Science Class 9 solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from R P Manchanda, Dr. Neha Jindal and, Ms. Archita Baruah Bhattacharyya Solutions for Chapter: Gravitation, Exercise 1: ASSESS YOURSELF with Hints & Solutions
Why do we feel lighter when we swim?
A hollow plastic ball is taken to the bottom of a trough of water and released there (see adjoining figure).
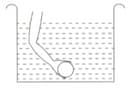
(a) What happens to the ball?
(b) Give reason for this phenomenon.
A wooden block is kept on a table top. The mass of the wooden block is and its dimensions are . Find the pressure exerted by the wooden block on the table top if it is made to lie on the table top with its sides of dimensions (a) and (b) .
State Archimedes' Principle. List its two applications.
When water is drawn from a well, a bucket feels heavier when it is drawn out of water or in the air than inside water. Why?
An object is suspended with a string which gets stretched. When the object is completely immersed in water, the extension of string decreases. Explain why it happens.
Lead has greater density than iron and both are denser than water. Is the buoyant force on a lead object greater than or lesser than or equal to the buoyant force on an iron object of the same volume? Explain your answer giving reason.
Define relative density of a solid. State its unit. How is it related to its density? Write mathematical expression for relative density. What conclusion do you draw if relative density of a substance is (a) greater than , (b) less than and (c) equal to ?
