Resnick & Halliday Solutions for Chapter: Potential Energy and Conservation of Energy, Exercise 1: Problems
Resnick & Halliday Physics Solutions for Exercise - Resnick & Halliday Solutions for Chapter: Potential Energy and Conservation of Energy, Exercise 1: Problems
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 8: Potential Energy and Conservation of Energy, Exercise 1: Problems with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Principles Of Physics International Student Version solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Resnick & Halliday Solutions for Chapter: Potential Energy and Conservation of Energy, Exercise 1: Problems with Hints & Solutions
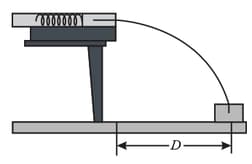
Two children are playing a game in which they try to hit a small box on the floor with a marble fired from a spring-loaded gun that is mounted on a table. The target box is horizontal distance from the edge of the table; see in the figure shown below. Bobby compresses the spring but the center of the marble falls short of the center of the box. How far should Rhoda compress the spring to score a direct hit? Assume that neither the spring nor the ball encounters friction in the gun.
At a Iunar base, a uniform chain hangs over the edge of a horizontal platform. A machine does of work in pulling the rest of the chain onto the platform. The chain has a mass of and a length of What length was initially hanging over the edge? On the Moon, the gravitational acceleration is of .
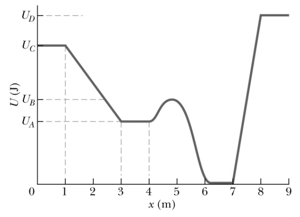
In the figure shown below shows a plot of potential energy versus position of a particle that can travel only along an -axis under the influence of a conservative force. The graph has these values: and . The particle is released at the point where forms a "potential hill" of height with kinetic energy What is the speed of the particle at (a) and
(b) ? What is the position of the turning point on (c) the right side and (d) the left side?
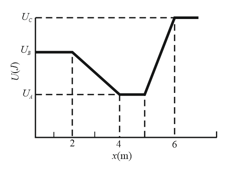
In the figure shown below, a plot of potential energy versus position of a particle that can travel only along an -axis (Non-conservative forces are not involved). Three values are and The particle is released at with an initial speed of , headed in the negative -direction.
(a) If the particle can reach what is its speed there and if it cannot, what is its turning point? What are the (b) magnitude and (c) direction of the force on the particle as it begins to move to the left of ? Suppose, instead, the particle is headed in the positive -direction when it is released at at speed . (d) If the particle can reach what is its speed there, and if it cannot, what is its turning point? What are the
(e) magnitude and (f) direction of the force on the particle as it begins to move to the right of ?
The potential energy of a diatomic molecule(a two-atom system like or ) is given by , where is the separation of the two atoms of the molecule and and are positive constants. This potential energy is associated with the force that binds the two atoms together. (a) Find the equilibrium separation - that is, the distance between the atoms at which the force on each atom is zero. Is the force repulsive (the atoms are pushed apart) or attractive (they are pulled together) if their separation is (b) smaller and (c) larger than the equilibrium separation?
A single conservative force, acts on a particle that moves along the -axis. The potential energy, associated with is given by, where, is in meters. At , the particle has a kinetic energy of .
(a) What is the mechanical energy of the system?
(b) Make a plot of as a function of for and on the same graph, draw the line that represents the mechanical energy of the system. Use part (b) to determine (c) the least value of the particle can reach and (d) the greatest value of the particle can reach. Use part (b) to determine (e) the maximum kinetic energy of the particle and (f) the value of at which it occurs.
(g) Determine an expression in newtons and meters for as a function of (h) For what (finite) value of is ?
A worker pushed a block along a level floor at a constant speed with a force directed below the horizontal. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the floor was , what were,
(a) The work done by the worker's force and
(b) The increase in thermal energy of the block- floor system?
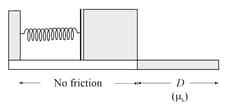
In the figure shown below, a block is accelerated from rest by a compressed spring of spring constant . The block leaves the spring at the spring's relaxed length and then travels over a horizontal floor with a coefficient of kinetic friction The frictional force stops the block in distance What are
(a) The increase in the thermal energy of the block-floor system
(b) The maximum kinetic energy of the block
(c) the original compression distance of the spring?