S L Arora Solutions for Chapter: Magnetic Effect of Current, Exercise 1: Problems For Practice
S L Arora Physics Solutions for Exercise - S L Arora Solutions for Chapter: Magnetic Effect of Current, Exercise 1: Problems For Practice
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 4: Magnetic Effect of Current, Exercise 1: Problems For Practice with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. New Simplified Physics (Vol 1) For Class 12 solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from S L Arora Solutions for Chapter: Magnetic Effect of Current, Exercise 1: Problems For Practice with Hints & Solutions
A shunt of is connected across a galvanometer of resistance . Find the fraction of the total current passing through the galvanometer.
It is required to pass only one‐tenth of the main current through a galvanometer having a resistance of . Calculate the length of the wire of specific resistance and area of cross‐section required to make a shunt for this purpose.
A galvanometer gives a full-scale deflection with a current of . It is converted into ammeter of range . Find the ratio of the resistance of the ammeter to the resistance of the shunt used.
A galvanometer has a resistance of . It gives a full-scale deflection for a current of . It is to be converted into an ammeter of range . The only shunt resistance available is of , which is not suitable for this conversion. Find the value of resistance that must be connected in series with the galvanometer (Figure) to get ammeter of desired range.
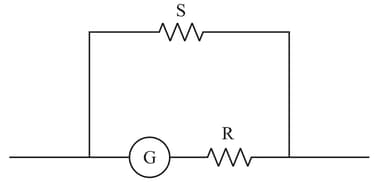
The circuit shown in Figure is used to measure the resistance . The ammeter reads and the voltmeter reads . The resistance of the ammeter is and that of the voltmeter is . Find the value of .
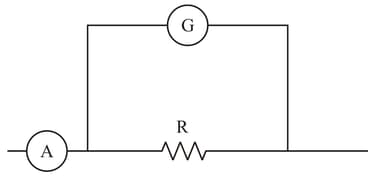
The scale of a galvanometer is divided into equal divisions. The galvanometer has the current sensitivity of divisions per and the voltage sensitivity of divisions per . How the galvano‐ meter can be designed to read (i) and (ii) ?
Two resistance coils of and respectively are connected in series across . A moving coil voltmeter of is connected in turn across each coil. What will it read in each case?
A battery of emf and internal resistance supplies a current through a coil of resistance . A voltmeter of resistance is used to measure the potential difference across the coil. What would be the reading on the voltmeter?
