SHORT ANSWER CONCEPTUAL PROBLEMS
S L Arora Physics Solutions for Exercise - SHORT ANSWER CONCEPTUAL PROBLEMS
Simple step-by-step solutions to SHORT ANSWER CONCEPTUAL PROBLEMS questions of Magnetic Effect of Current from New Simplified Physics (Vol 1) For Class 12. Also get 3D topic explainers, cheat sheets, and unlimited doubts solving on EMBIBE.
Questions from SHORT ANSWER CONCEPTUAL PROBLEMS with Hints & Solutions
The magnitude F of the force between two straight parallel current carrying conductors kept at a distance d apart in air is given by , where and are the currents flowing through the two wires. Use this expression, and the sign convention that the: "Force of attraction is assigned a negative sign and force of repulsion is assigned a positive sign". Draw graphs showing dependence of on
(i) when is kept constant.
The magnitude F of the force between two straight parallel current carrying conductors kept at a distance d apart in air is given by , where and are the currents flowing through the two wires. Use this expression, and the sign convention that the: "Force of attraction is assigned a negative sign and force of repulsion is assigned a positive sign". Draw graphs showing dependence of on
(ii) when the product is maintained at a constant positive value.
The magnitude F of the force between two straight parallel current carrying conductors kept at a distance d apart in air is given by , where and are the currents flowing through the two wires. Use this expression, and the sign convention that the: "Force of attraction is assigned a negative sign and force of repulsion is assigned a positive sign". Draw graphs showing dependence of on
(ii) when the product is maintained at a constant negative value.
The current flowing in the galvanometer when the key is kept open is . On closing the key , the current in the galvanometer becomes , where is an integer. Obtain an expression for resistance of the galvanometer in terms of and . To what form does this expression reduce when the value of is very large as compared to ?
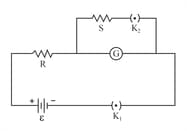
Why is it necessary to use (ii) a cylindrical soft iron core in a galvanometer ? Can a galvanometer as such be used for measuring the current ? Explain.
Why is it that while using a moving coil galvanometer as a voltmeter a high resistance in series is required whereas in an ammeter a shunt is used ?
Compare a voltmeter and an ammeter.
Define current sensitivity and voltage sensitivity of a galvanometer. Increasing the current sensitivity may not necessarily increase the voltage sensitivity of a galvanometer. Justify.
