Sarvesh K Verma Solutions for Chapter: Geometry, Exercise 2: Introductory Exercise
Author:Sarvesh K Verma
Sarvesh K Verma Quantitative Aptitude Solutions for Exercise - Sarvesh K Verma Solutions for Chapter: Geometry, Exercise 2: Introductory Exercise
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 12: Geometry, Exercise 2: Introductory Exercise with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Quantum CAT Also Useful for XAT | SNAP | CMAT | MAT solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Sarvesh K Verma Solutions for Chapter: Geometry, Exercise 2: Introductory Exercise with Hints & Solutions
MEDIUM
CAT
IMPORTANT
In , , . If is the angle bisector of . Then is-
EASY
CAT
IMPORTANT
The incentre of a triangle is determined by
EASY
CAT
IMPORTANT
If in a is the circumcentre, then:
EASY
CAT
IMPORTANT
In a right angled and is the perpendicular on hypotenuse if and , then is equal to :
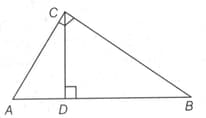
EASY
CAT
IMPORTANT
The internal bisector of and of meet at O. If , then is-
MEDIUM
CAT
IMPORTANT
is a triangle and is drawn parallel to cutting other sides and at respectively. If , and then is _____
EASY
CAT
IMPORTANT
ABC is an isoceles triangles with AB = AC, side BA is produced to D such that AB = AD. Find ∠BCD.
