NCERT Solutions for Chapter: Carbon and its Compounds, Exercise 1: Exercise
NCERT Science Solutions for Exercise - NCERT Solutions for Chapter: Carbon and its Compounds, Exercise 1: Exercise
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 4: Carbon and its Compounds, Exercise 1: Exercise with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Science Textbook of Competency Based Questions for Class X solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from NCERT Solutions for Chapter: Carbon and its Compounds, Exercise 1: Exercise with Hints & Solutions
The picture shows the incomplete chain structure of a carbon compound. The second carbon atom has two free electrons.
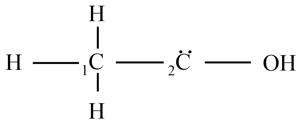
How many oxygen atoms can combine with the second carbon atom to complete the structure?
Which of these molecules contains a double bond?
A part of a homologous series is shown below.
Which of these compounds is a part of the series shown above?
The picture shows the bonds between atoms in two allotropes of carbon.
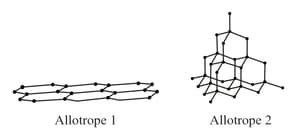
Which allotrope is harder? Explain your answer.
On undergoing complete combustion in an adequate supply of oxygen, an organic compound produces only carbon dioxide and water vapour as the products.
Based on this information, Which of the following homologous series could the compound belong to?
alkanes
alcohols
aldehydes
A compound with which of the following functional groups is most likely to cause the decomposition of baking soda to produce carbon dioxide?
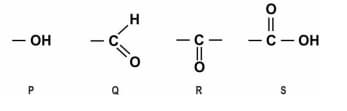
mole of ethene and mole of ethyne are separately made to completely undergo addition reaction to form the respective saturated compound.
Which of the following will be different for the two reactions?
The number of moles of the saturated compound formed.
The number of moles of the hydrogen consumed.
Heating an alcohol with concentrated sulphuric acid results in the dehydration of the alcohol to give the alkene as shown by the reaction of ethanol to give ethene.
Pramila heated -butanol (shown below) with concentrated sulphuric acid.
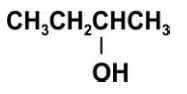
Write the structural formulae of all the possible products of the reaction.
