R P Goyal and S P Tripathi Solutions for Chapter: Refraction Through a Lens, Exercise 2: EXERCISE-5(B)
R P Goyal Physics Solutions for Exercise - R P Goyal and S P Tripathi Solutions for Chapter: Refraction Through a Lens, Exercise 2: EXERCISE-5(B)
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 5: Refraction Through a Lens, Exercise 2: EXERCISE-5(B) with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Selina Icse Concise Physics For Class 10 solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from R P Goyal and S P Tripathi Solutions for Chapter: Refraction Through a Lens, Exercise 2: EXERCISE-5(B) with Hints & Solutions
What are the three principal rays that are drawn to construct the ray diagram for the image formed by a lens? Draw diagrams to support your answer.
In the diagrams below, represents the principal axis, the optical centre and the focus of the lens. Complete the path of the rays and as they emerge out of the lens.
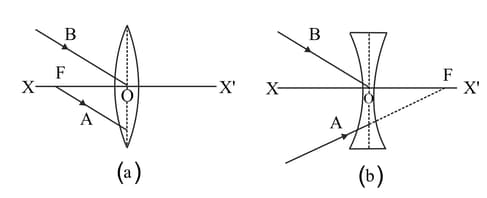
Can a concave lens forms an image of size two times that of the object? Give reason.
Give two characteristics of the image formed by a concave lens.
Give two characteristics of the virtual image formed by a convex lens.
Complete the following table.
| Type of lens | Position of object | Nature of image | Size of image |
| convex | Between optic centre and focus | ||
| convex | At focus | ||
| concave | At infinity | ||
| concave | At any distance |
State the changes in the position, size and nature of the image of an object when brought from infinity up to a convex lens. Illustrate your answer by drawing ray diagrams.
State the changes in the position, size and nature of the image of an object when brought from infinity up to a concave lens. Illustrate your answer by drawing diagrams.
