Sergey Bylikin, Gary Horner and, Brian Murphy Solutions for Chapter: Biochemistry, Exercise 6: Questions
Sergey Bylikin Chemistry Solutions for Exercise - Sergey Bylikin, Gary Horner and, Brian Murphy Solutions for Chapter: Biochemistry, Exercise 6: Questions
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 23: Biochemistry, Exercise 6: Questions with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. Oxford IB Diploma Programme Chemistry Course Companion solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Sergey Bylikin, Gary Horner and, Brian Murphy Solutions for Chapter: Biochemistry, Exercise 6: Questions with Hints & Solutions
State the name of one non-reducing sugar.
Lactulose is a synthetic, non-digestible disaccharide that is used in the treatment of chronic constipation and liver disease. This disaccharide contains the residues of galactose and fructose. The formula of α-lactulose is given below
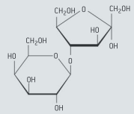
Identify the glycosidic link in lactulose by drawing a circle around it.
Lactulose is a synthetic, non-digestible disaccharide that is used in the treatment of chronic constipation and liver disease. This disaccharide contains the residues of galactose and fructose. The formula of α-lactulose is given below
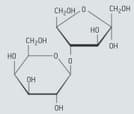
Suggest whether lactulose is a reducing or non-reducing sugar. Explain your answer.
In making candy or sugar syrup, sucrose is boiled in water with a small amount of organic acid, such as citric acid from lemon juice. Explain why the product mixture tastes sweeter than the initial sucrose solution.
Explain what feature of the structure of glycerol (propane-1,2,3-triol) allows fatty acid molecules to become attached to it to make fats, and state the name of the reaction by which this occurs.
Lactose is a typical disaccharide. Suggest a reason why fatty acids can be attached to it.
The fatty acids in olestra are smaller than those in cooking fats. Suggest a reason for this.
State the name of the two polymeric forms of starch.
