Exercise 1
Embibe Experts Social Science Solutions for Exercise 1
Simple step-by-step solutions to Exercise 1 questions of The French Revolution from Social Science Textbook of Competency Based Questions for Class IX. Also get 3D topic explainers, cheat sheets, and unlimited doubts solving on EMBIBE.
Questions from Exercise 1 with Hints & Solutions
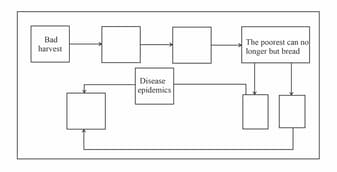
Fill in the boxes in the given image with appropriate terms from among the following:
Food riots, scarcity of grain, increased number of deaths, rising food prices, weaker bodies.
The Declaration of Rights of Man and Citizen
- Men are born and remain free and equal in rights
- The aim of every political association is the preservation of the natural and inalienable rights of man; these are liberty, property, security and resistance to oppression
- The source of all sovereignty resides in the nation; no group or individual may exercise authority that does not come from the people
- Liberty consists of the power to do whatever is not injurious to others
- The law has the right to forbid only actions that are injurious to society
- Law is the expression of the general will. All citizens have the right to participate in its formation, personally or through their representatives. All citizens are equal before it
- No man may be accused, arrested or detained, except in cases determined by the law
- Every citizen may speak, write and print freely; he must take responsibility for the abuse of such liberty in cases determined by the law
- For the maintenance of the public force and for the expenses of administration, a common tax is indispensable; it must be assessed equally on all citizens in proportion to their means
- Since the property is a sacred and inviolable right, no one may be deprived of it, unless a legally established public necessity requires it. In that case, just compensation must be given in advance
Refer to Source given above and compare the views of Desmoulins and Robespierre and answer the following questions.
1. How does each one understand the use of state force? What does Robespierre mean by ‘the war of liberty against tyranny?
2. How does Desmoulins perceive liberty? What did the constitutional laws on the rights of individuals lay down? Discuss your views on the subject in class.
Identify the symbols in the image which stand for liberty, equality and fraternity.








What were the outcomes of the French Revolution?
Compare the manifesto drafted by Declaration of the Rights of Man and Citizen (Source A) with the Olympe de Gouges (Source B).
Source A
The Declaration of Rights of Man and Citizen are as follows:
- Men are born and remain free and equal in rights.
- The aim of every political association is the preservation of the natural and inalienable rights of man; these are liberty, property, security and resistance to oppression.
- The source of all sovereignty resides in the nation; no group or individual may exercise authority that does not come from the people.
- Liberty consists of the power to do whatever is not injurious to others.
- The law has the right to forbid only actions that are injurious to society.
- Law is the expression of the general will. All citizens have the right to participate in its formation, personally or through their representatives. All citizens are equal before it.
- No man may be accused, arrested or detained, except in cases determined by the law.
- Every citizen may speak, write and print freely; he must take responsibility for the abuse of such liberty in cases determined by the law.
- For the maintenance of the public force and for the expenses of administration a common tax is indispensable; it must be assessed equally on all citizens in proportion to their means.
- Since the property is a sacred and inviolable right, no one may be deprived of it, unless a legally established public necessity requires it.
Source B
Basic rights set forth in Olympe de Gouges’ Declaration are as follows:
- The woman is born free and remains equal to the man in rights.
- The goal of all political associations is the preservation of the natural rights of woman and man: These rights are liberty, property, security, and above all resistance to oppression.
- The source of all sovereignty resides in the nation, which is nothing but the union of woman and man.
- The law should be the expression of the general will; all female and male citizens should have a say either personally or by their representatives in its formulation; it should be the same for all. All female and male citizens are equally entitled to all honours and public employment according to their abilities and without any other distinction than that of their talents.
- No woman is an exception; she is accused, arrested, and detained in cases determined by law. Women, like men, obey this rigorous law.
Read the statements below carefully and choose the correct option.
Statement 1: France's Constitution of began with a Declaration of the Rights of Woman and Citizen.
Statement 2: The main objective of the drafting the first constitution in was to give more power to the monarch in France.
Statement 3: Under the Old Regime in France, the first two estates were exempted from paying taxes.
Describe the legacy of the French Revolution for the peoples of the world during the nineteenth and the twentieth centuries.

Marat addressing the people. This is a painting by Louis-Leopold Boilly.
Describe the surrounding scene. Account for his great popularity. What kinds of reactions would a painting like this produce among viewers in the Salon?
