Subject Experts Solutions for Exercise 2: HOTS HIGHER ORDER THINKING SKILLS
Subject Experts Biology Solutions for Exercise - Subject Experts Solutions for Exercise 2: HOTS HIGHER ORDER THINKING SKILLS
Attempt the free practice questions from Exercise 2: HOTS HIGHER ORDER THINKING SKILLS with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. MTG OBJECTIVE NCERT AT YOUR FINGERTIPS BIOLOGY CLASS XI + XII solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Subject Experts Solutions for Exercise 2: HOTS HIGHER ORDER THINKING SKILLS with Hints & Solutions
Refer to the given graph carefully and answer the following question.
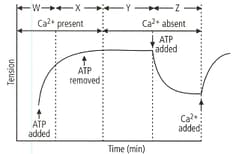
Which of the labelled parts on the graph represents rigor mortis?
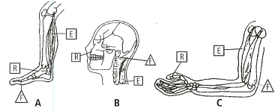
Refer to the given figures, and arrange them in an order of first-class lever, second-class lever, and third-class lever.
The given graph shows the length-tension curve for a typical vertebrate sarcomere.
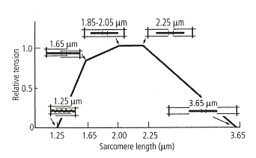
By analysing the graph, what can you deduce regarding muscle contraction?
(i) Neither the myosin filaments nor the actin thin filaments change in length when a sarcomere shortens or is stretched. Instead, it is the extent of overlap between actin and myosin filaments that changes.
(ii) The total tension produced by a sarcomere is proportional to the total number of cross-bridges that can interact with actin filaments, and this number, in turn, is proportional to the amount of overlap between thick and thin filaments.
(iii) The tension produced by the muscle is maximal when the overlap between thick and thin filaments allows the largest number of myosin cross-bridges to bind to actin.
(iv) Tension drops off with increased length because the thick and thin filaments overlap less and fewer cross-bridges can bind.
(v) Tension drops off with decreased length because thin filaments at the two ends of the sarcomere begin to collide with each other, preventing further shortening.
Long-distance, competitive runners are usually small and wiry and run more slowly than sprinters, who run much shorter distances and generally have a large bulk of muscles. Which of the following best explains the differences between the two types of runners?
Which of the following correctly characterises a "fast oxidative" type of skeletal muscle fibre?
