Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Electricity and Circuits, Exercise 1: Exercise
Embibe Experts Science Solutions for Exercise - Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Electricity and Circuits, Exercise 1: Exercise
Attempt the free practice questions on Chapter 12: Electricity and Circuits, Exercise 1: Exercise with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. THINK ABOVE AND BEYOND SCIENCE PRACTICE BOOKS solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Embibe Experts Solutions for Chapter: Electricity and Circuits, Exercise 1: Exercise with Hints & Solutions
Two different ways are shown below to connect a bulb with a cell.
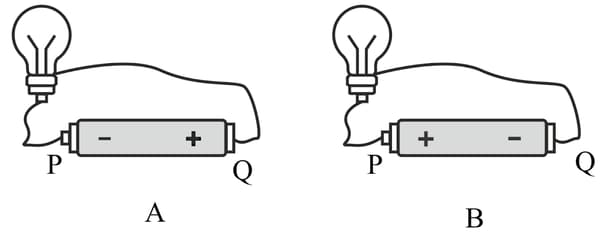
What will be the direction of the current through the bulb in both the cases. (Q to P or P to Q)?
In which case the bulb will glow?
Does the brightness of the glowing bulb depend on the direction of current through it?
Look carefully at the circuit given below:
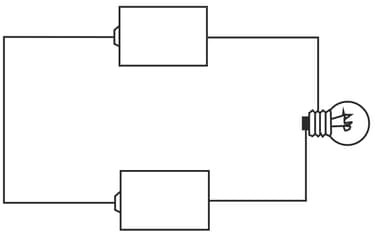
(a) In the above circuit, will the bulb light up?
(b) What is the reason for your answer?
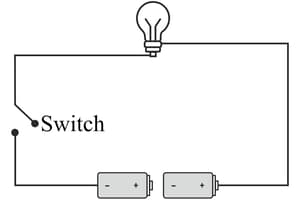
What are the two things that must be done to make the bulb light up in the following case?
What makes the human body conduct electricity?
The diagram shows an electric circuit.
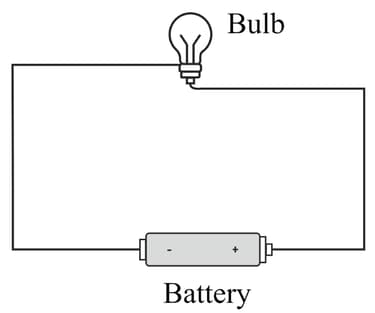
What will happen if another battery is added to the circuit?
What is the direction of the flow of electric current in the circuit?
The positive terminal of an electric cell was connected to a torch bulb fitted in a bulb holder. The other end of bulb holder was connected to a crocodile clip. The negative terminal of cell was connected to another crocodile clip by a wire. When a material X was held between the two free ends of the crocodile clips, the bulb did not glow but when another material Y was held between the two free ends of the crocodile clips, the bulb started glowing.
What is the general name of the materials like (i) X, and (ii) Y?
Name one material each which could behave like (i) X, and (ii) Y
Which part/parts of an electric plug is /are made of materials like (i) X, and (ii) Y?
A and B are two devices. Both these devices have two terminals each. If the two terminals of device A are connected directly by a wire, nothing happens but when the two terminals of device B are connected by a wire directly, it gets damaged quickly. When the two terminals of device B are connected to the two terminals of device A, by copper wires, then part C of device A gets heated and glows to produce light.
What could be device A?
What could be device B?
Name the part C of device A.
In which device, A or B, the two terminals are marked + and -?
A student made a circuit by using an electric cell, a switch, a torch bulb (fitted in the bulb holder) and copper connecting wires. When he 'turned on' the switch, the torch bulb did not glow at all.
The student checked the circuit and found that all the wire connections were intact. What could be the possible reason for the torch bulb not glowing even when the circuit appears to be complete?
The student checked the circuit and found that all the wire connections were tight. What could have caused the above condition?
