Umakant Kondapure, Collin Fernandes, Nipun Bhatia, Vikram Bathula and, Ketki Deshpande Solutions for Chapter: Circular Motion, Exercise 3: Competitive Thinking
Umakant Kondapure Physics Solutions for Exercise - Umakant Kondapure, Collin Fernandes, Nipun Bhatia, Vikram Bathula and, Ketki Deshpande Solutions for Chapter: Circular Motion, Exercise 3: Competitive Thinking
Attempt the practice questions on Chapter 9: Circular Motion, Exercise 3: Competitive Thinking with hints and solutions to strengthen your understanding. MHT-CET TRIUMPH Physics Multiple Choice Questions Part - 1 Based on Std. XI & XII Syllabus of MHT-CET solutions are prepared by Experienced Embibe Experts.
Questions from Umakant Kondapure, Collin Fernandes, Nipun Bhatia, Vikram Bathula and, Ketki Deshpande Solutions for Chapter: Circular Motion, Exercise 3: Competitive Thinking with Hints & Solutions
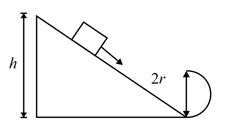
A block follows the path as shown in the figure from height . If radius of circular path is , then relation holds good to complete full circle is
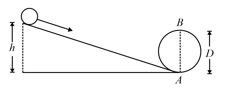
A body initially at rest and sliding along a frictionless track from a height (as shown in the figure) just completes a vertical circle of diameter . The height is equal to
A particle moves in a circle of radius with constant speed and time period . The acceleration of the particle is
A uniform circular disc of radius at rest is free to turn about an axis which is perpendicular to its plane and passes through its centre. It is subjected to a torque which produces a constant angular acceleration of . Its net acceleration in at the end of is approximately
A particle is moving with a uniform speed in a circular orbit of radius in a central force inversely proportional to the power of . If the period of rotation of the particle is , then
A particle is moving in a circular path of radius under the action of an attractive potential . Its total energy is
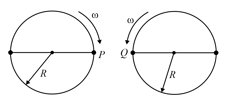
Two identical discs of the same radius are rotating about their axes in opposite directions with the same constant angular speed . The discs are in the same horizontal plane. At time , the points are facing each other as shown in the figure. The relative speed between the two points . As a function of time, it is best represented by
A wheel of circumference is at rest on the ground. When the wheel rolls forward through half a revolution, then the displacement of initial point of contact will be
