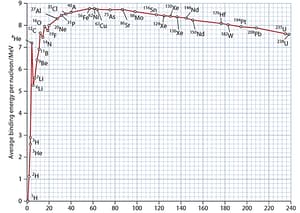
Using the binding energy curve (Average binding energy per nucleon vs mass number) shown above explain why energy is released in nuclear fusion.


Important Questions on Atomic, Nuclear and Particle Physics
Explain, in terms of quarks, the difference between a baryon and a meson.
In a copy of the table shown below, write 'yes' to identify the interaction(s) that apply to hadrons and to leptons.
| Strong | Weak | |
| hadrons | ||
| leptons |
Copy and complete the Feynman diagram to represent the beta minus decay of neutron, making sure that you label all particles involved.
The muon decays according to . A Feynman diagram for this decay is shown below.
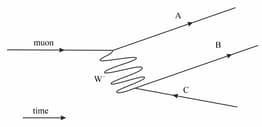
Identify the three unlabelled particles in the diagram.
The muon decays according to . A Feynman diagram for this decay is shown below.
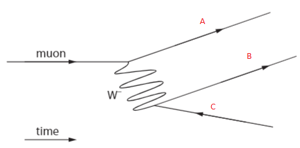
Use the above diagram to construct a new Feynman diagram representing the scattering of electron anti-neutrino off a muon.
Write down the reaction equation representing the decay , which is anti-particle of the .
The interaction responsible for the decay of the muon has a very short range. State the property of the exchange particle that is responsible for the short range.
