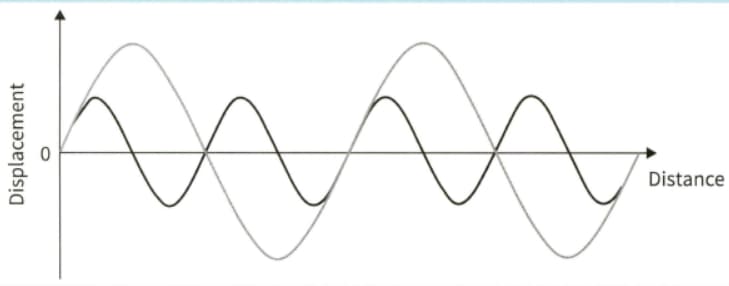
(a) Copy the waves shown in the diagram onto a sheet of graph paper and use the principle of superposition to sketch the resultant wave.


Important Questions on Superposition of Waves
(b) Compare the wavelength of the resultant wave with that of the component waves.
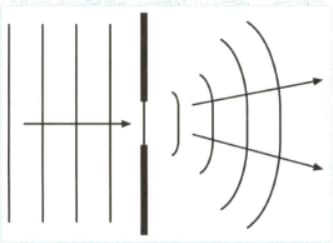
State how the diffracted pattern will change when:
(a) The wavelength of the incident wave is increased
State how the diffracted pattern will change when:
(b) The wavelength of the incident wave is decreased.
A constant frequency signal from a signal generator is fed to two loudspeakers placed apart. A student, who is away from the loudspeakers, walks across in a line parallel to the line between the loudspeakers. The student measures the distance between successive spots of loudness to be . Calculate:
(a) The wavelength of the sound
A constant frequency signal from a signal generator is fed to two loudspeakers placed apart. A student, who is away from the loudspeakers, walks across in a line parallel to the line between the loudspeakers. The student measures the distance between successive spots of loudness to be . Calculate:
(b) The frequency of the sound (assume the speed of sound is )
One of the spectral lines from a hydrogen discharge lamp has wavelength . This light is incident normally at a diffraction grating with lines .
Calculate the angles for the first- and second-order maxima for this light
