(a) State two similarities and two differences between progressive waves and stationary waves.

Important Questions on Stationary Waves
(b) Explain why it is better to measure the distance across several nodes.
For sound waves of frequency , it is found that two nodes are separated by , with three antinodes between them.
(b) Use the wave equation to determine the speed of sound in air.
(b) This diagram shows an experiment to measure the speed of a sound in a string. The frequency of the vibrator is adjusted until the stationary wave shown is formed.
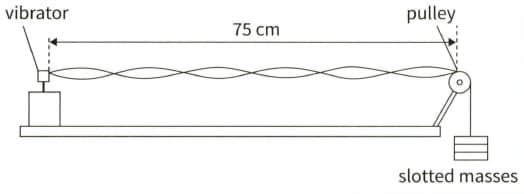
(i) On a copy of the diagram, mark a node (label it N) and an antinode (label it A).
(a) Explain what is meant by:
(i) A coherent source of waves.
(a) Explain what is meant by:
(ii) Phase difference.
The speed of a transverse wave on a stretched wire is given by the expression
Where is the tension in the wire.
A length of wire is stretched between two fixed point. The tension in the wire is . The wire is gently plucked from the middle. A stationary wave, of fundamental frequency , is produced.
The tension in the wire is now increased to . The percentage uncertainty in new tension is . The length of the wire is unchanged. Calculate the new value for the fundamental frequency when the wire is plucked in the middle. Your answer must include the absolute uncertainty written to an appropriate number of significant figures.
