EASY
Earn 100
moles of helium gas is mixed with moles of hydrogen molecules (taken to be rigid). Find the molar specific heat of the mixture at constant volume.
(a)
(b)
(c)
(d)
50% studentsanswered this correctly
Important Questions on Thermodynamics
MEDIUM
EASY
MEDIUM
What will be the molar specific heat at constant volume of an ideal gas consisting of rigid diatomic molecules?
EASY
MEDIUM
EASY
MEDIUM
An ideal gas undergoes a four step cycle as shown in the diagram below. During this cycle, heat is absorbed by the gas in:
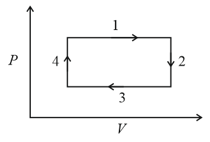
MEDIUM
[Given that
HARD
HARD
For a monoatomic ideal gas following the cyclic process shown in the vs plot, identify the incorrect option:

EASY
(Take gas constant )
MEDIUM
Match the following: (where is gas constant)
| Column I | Column II | ||
| (a) | Molar specific heat of helium gas at constant volume | (i) | |
| (b) | Molar specific heat of oxygen at constant volume | (ii) | |
| (c) | Molar specific heat of carbon dioxide at constant volume | (iii) | |
| (d) | Molar specific heat of hydrogen at constant pressure | (iv) |
HARD
EASY
EASY
EASY
EASY
MEDIUM
EASY

