A battery of e.m.f. produces a steady current of for minutes. Calculate the charge that it supplied.

Important Questions on Electric Current, Potential Difference and Resistance
A battery of e.m.f. produces a steady current of for minutes. Calculate:
(b) The energy that it transferred.
This diagram shows the electrolysis of copper chloride.
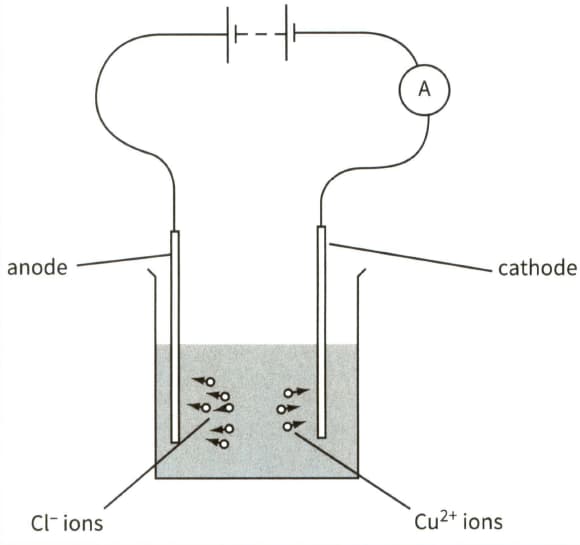
On a copy of the diagram, mark the direction of the conventional current in the electrolyte. Label it conventional current.
This diagram shows the electrolysis of copper chloride.
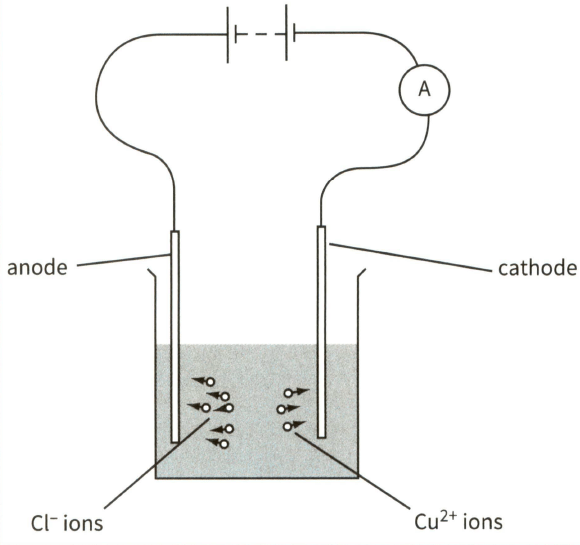
Mark the direction of the electron flow in the connecting wires. Label this electron flow.
This diagram shows the electrolysis of copper chloride.
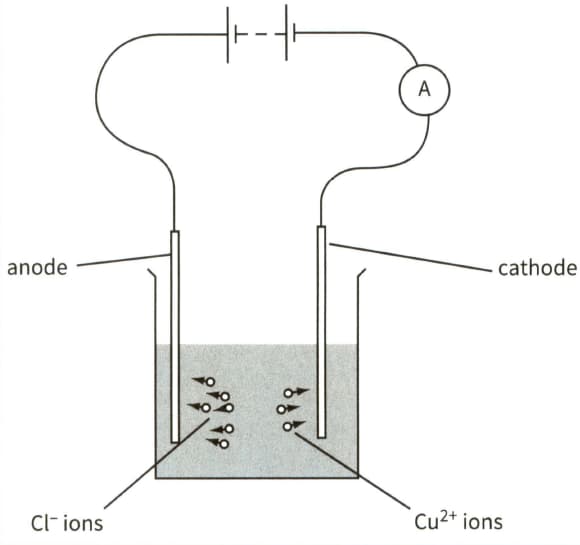
(b) In a time period of 8 minutes, chloride ions are neutralised and liberated at the anode and copper ions are neutralised and deposited on the cathode.
(i) Calculate the total charge passing through the electrolyte in this time.
This diagram shows the electrolysis of copper chloride.
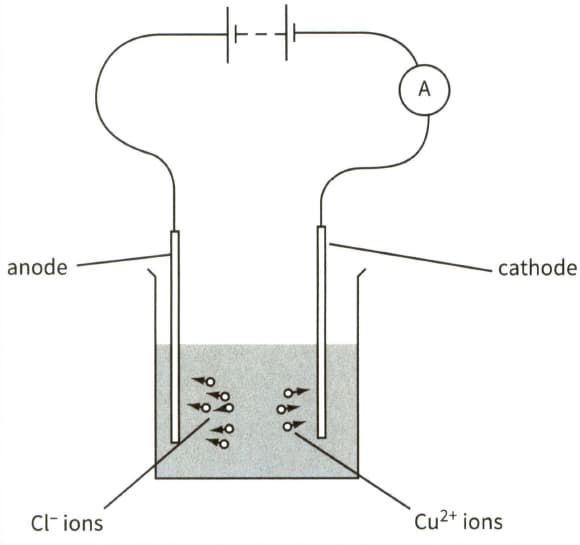
(b) In a time period of 8 minutes, chloride ions are neutralised and liberated at the anode and copper ions are neutralised and deposited on the cathode.
(ii) Calculate the current in the circuit.
This diagram shows an electron tube. Electrons moving from the cathode to the anode constitute a current. The current in the ammeter is .
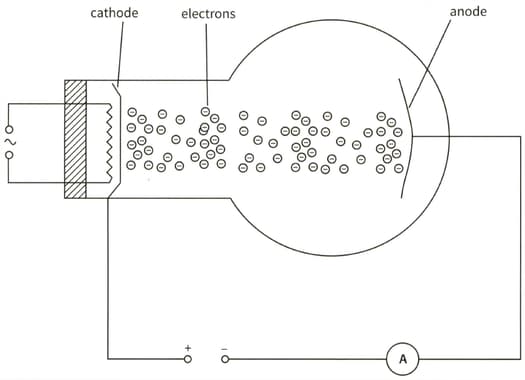
(a) Calculate the charge passing through the ammeter in 3 minutes.
