A block of mass placed on ground is pulled by a string by applying force:
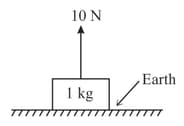
(i) Draw of block.
(ii) Give action–reaction pair involved in the above problem.


Important Questions on Laws of Motion
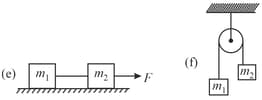
Draw free body diagrams for masses and shown in the figure. Identify all action–reaction pairs between two blocks. The pulley is frictionless and massless and all surfaces are smooth.
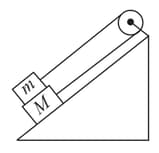
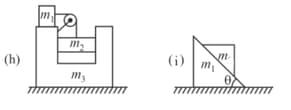
Draw the for the following individual parts of the systems:
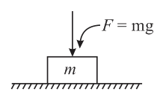
A block of mass is placed on ground and an additional force is applied on the block as shown in the figure. Calculate contact force between ground and block.
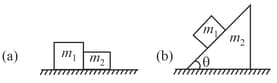
Two blocks of masses and are placed on the ground as shown in the figure. Two forces of magnitude act on and in opposite directions.
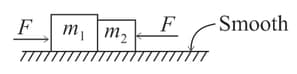
(i) Draw of masses and .
(ii) Calculate the contact force between and .
(iii) What will be the value of normal force between and .
(iv) Calculate force exerted by ground surface on mass and
A sphere of mass , radius placed between two vertical walls having separation which is slightly greater than :
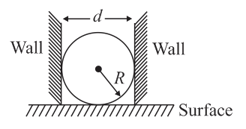
(i) Calculate force exerted by walls on the sphere.
(ii) Calculate force exerted by ground surface on the sphere.
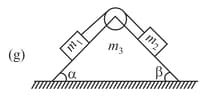
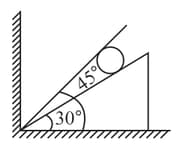
A spherical ball of mass rests between two planes which make angles of and , respectively, with the horizontal. The system is in equilibrium. Find the normal forces exerted on the ball by each of the planes. The planes are smooth.
A one meter long massless string fixed with a wall is pulled horizontally by applying a force of magnitude . Calculate:
(a) the tension at a point away from wall,
(b) the tension at a point away from wall,
(c) force exerted by string on the rigid support.
A block of mass is suspended by a string of mass , length as shown in the figure . Calculate:
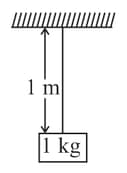
(a) the tension in string at its lowest point,
(b) the tension in string at its mid-point,
(c) force exerted by support on string.
