A coil is connected to a galvanometer. When the N-pole of a magnet is pushed into the coil, the galvanometer deflected to the right. What deflection, if any, is observed when: the S-pole is inserted?

Important Questions on Magnetic Effect of Electric Current
A coil is connected to a galvanometer. When the N-pole of a magnet is pushed into the coil, the galvanometer deflected to the right. What deflection, if any, is observed when: the magnet is at rest in the coil?
State three ways of increasing the deflection on the galvanometer.
When the magnet shown in the diagram below is moving towards the coil, the galvanometer gives a reading to the right.
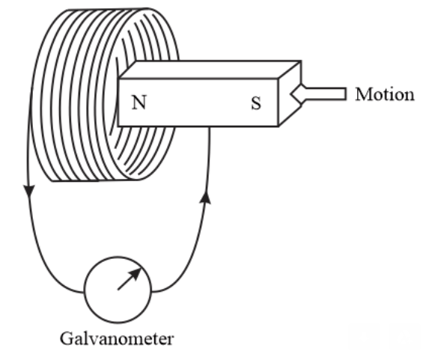
What is the name of the effect being produced by the moving magnet?
When the magnet shown in the diagram below is moving towards the coil, the galvanometer gives a reading to the right.
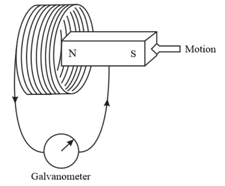
State what happens to the reading shown on the galvanometer when the magnet is moving away from the coil.
When the magnet shown in the diagram below is moving towards the coil, the galvanometer gives a reading to the right.
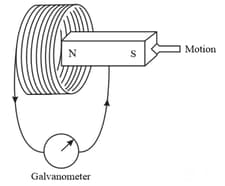
The original experiment is repeated. This time the magnet is moved towards the coil at a great speed. State two changes you would notice in the reading on the galvanometer.
The wire in figure below is being moved downwards through the magnetic field so as to produce induced current.
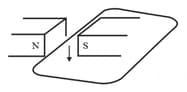
What would be the effect of: moving the wire at a higher speed?
The wire in figure below is being moved downwards through the magnetic field so as to produce induced current.
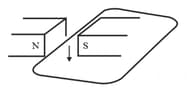
What would be the effect of: moving the wire upwards rather than downwards?
The wire in figure below is being moved downwards through the magnetic field so as to produce induced current.
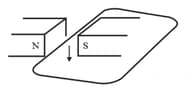
What would be the effect of: using a stronger magnet?
