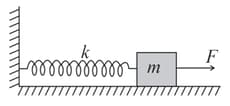
A constant force produces maximum velocity on the block connected to the spring of force constant as shown in the figure. When the force constant of spring becomes , then find the maximum velocity of the block. Assume that initially the spring is in a relaxed state.


Important Questions on Simple Harmonic Motion
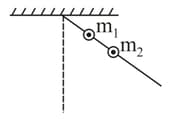
Two point masses and are fixed to a light rod hinged at one end. The masses are at distances and , respectively, from the hinge. Find the time period of oscillation (small amplitude) of this system in seconds if .
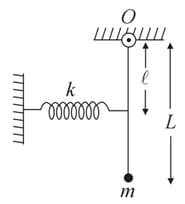
A particle of mass is suspended at the lower end of a thin rod of negligible mass. The upper end of the rod is free to rotate in the plane of the page about a horizontal axis passing through the point . The spring is undeformed when the rod is vertical as shown in figure. If the period of oscillation of the system is when it is slightly displaced from its mean position, then find . Take, and .
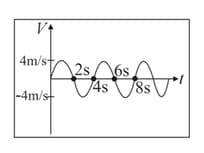
If velocity of a particle moving along a straight line changes sinusoidally with time as shown in the given graph, find the average speed over time interval, , being any positive integer.
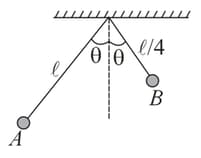
Two simple pendulums and having lengths and , respectively, are released from the position as shown in figure. Calculate the time after which the release of the two strings become parallel for the first time. The angle is very small.
Two non–viscous, incompressible and immiscible liquids of densities and are poured into the two limbs of a circular tube of radius and small cross–section kept fixed in a vertical plane as shown in fig. Each liquid occupies one–fourth the circumference of the tube.
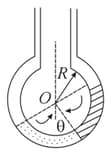
(a) Find the angle that the radius to the interface makes with the vertical in equilibrium position.
(b) If the whole liquid column is given a small displacement from its equilibrium position, show that the resulting oscillations are simple harmonic. Find the time period of these oscillations.
Two identical balls and , each of mass , are attached to two identical massless springs. The spring–mass system is constrained to move inside a rigid smooth pipe bent in the form of a circle as shown in the figure. The pipe is fixed in a horizontal plane. The centres of the balls can move in a circle of radius . Each spring has a natural length of and spring constant . Initially, both the balls are displaced by an angle radian with respect to the diameter of the circle (as shown in fig.) and released from rest.
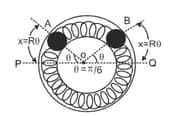
(i) Calculate the frequency of oscillation of ball .
(ii) Find the speed of ball when and are at the two ends of the diameter .
(iii) What is the total energy of the system?
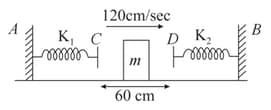
Two light springs of force constants and and a block of mass are in one line on a smooth horizontal table such that one end of each spring is fixed to rigid supports and the other end is free as shown in the figure. The distance between the free ends of the spring is . If the block moves along with a velocity in between the springs, calculate the period of oscillation of the block .
Two wheels which are rotated by some external source with constant angular velocity in opposite directions as shown in figure. A uniform plank of mass is placed on it symmetrically. The friction coefficient between each wheel and the plank is . Find the frequency of oscillations, when plank is slightly displaced along its length and released.