A convex lens is also known as converging lens.
Important Questions on Refraction through Lens
An object is placed between and on the principal axis of a converging lens as shown in the diagram.
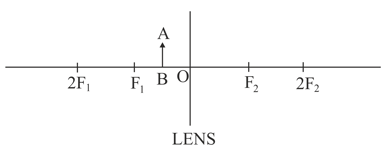
Copy the diagram and by using three standard rays starting from point , obtain an image of the object .
A virtual, diminished image is formed when an object is placed between the optical centre and the principal focus of a lens.
(i) Name the type of lens which forms the above image.
(ii) Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image with the above stated characteristics.
An object is placed at a distance in front of a convex lens of focal length .
(i) Calculate the distance of the image from the lens.
(ii) Calculate the magnification of the image.
Draw the given diagram in your answer book and complete it for the path of ray of light beyond the lens.
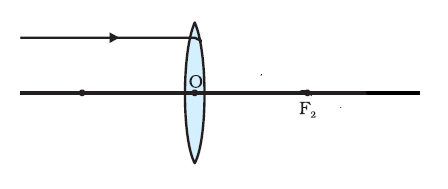
Draw the given diagram in your answer book and complete it for the path of light beyond the lens.
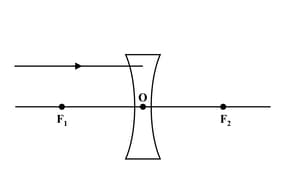
Define the terms converging and diverging lenses.
To find the image for varying object distances in case of a convex lens, a student obtains on a screen a sharp image of a bright object placed very far from the lens. After that he gradually moves the object towards the lens and each time focuses its image on the screen.
(a) In which direction-towards or away from the lens does he moves the screen to focus the object?
(b) What happens to the size of image-does it increase or decrease?
(c) What happens when he moves the object very close to the lens?
Each lens has a point, a ray passing through it goes without deviation. What is the name of that point and where is it located?