A convex spherical refracting surface of refractive index forms the image of an object distant from it at a distance of on the same side as the object. What is the radius of curvature of the surface?

Important Questions on Refraction of Light at Spherical Surfaces : Lenses
An empty spherical flask of diameter is placed in water . A parallel beam of light strikes the flask. Where will it appear to come from to an observer within the flask?
A point-object is placed in air at from a concave spherical surface of radius of curvature and refractive index . Locate the image.
A point-object is below the concave meniscus of water of radius of curvature . Locate the image.
A glass sphere of radius has a small bubble from its centre. The bubble is viewed along a diameter of the sphere, from the side on which it lies. How far from the surface will it appear? Refractive index of glass is .
An air bubble is seen inside a solid sphere of glass of Diameter at a distance of From the surface of the sphere (on seeing along the diameter). Determine the real position of the bubble inside the sphere.
One end of a cylindrical rod of glass shown in the figure is given a spherical shape of the radius
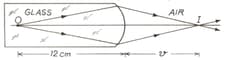
. On the left side of this end is placed an object at a distance of . Find out the distance () of the image.
The radii of curvature of a double convex lens are and and the refractive index of its glass is . Calculate the focal length of the lens.
The radii of curvature of a double concave lens are and and the refractive index of its glass is . Calculate the focal length of the lens.
