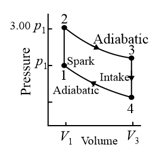
A gas sample undergoes a reversible isothermal expansion. Figure (as shown below) gives the change in the entropy of the gas versus the final volume of the gas. The scale of the vertical axis is set by . How many moles are in the sample?


Important Questions on Entropy and the Second Law of Thermodynamics
Calculate the entropy change of the system during this process. (Heat of fusion for water is undefined) The system is then returned to the initial equilibrium state in an irreversible process (say, by using a Bunsen burner). Calculate the entropy change of the system during this process. Are your answers consistent with the second law of thermodynamics?
Suppose of a monatomic ideal gas is taken from initial pressure and volume , through two steps: an isothermal expansion to volume and a pressure increase to at constant volume. What is for step and step ? What is for step and step ? For the full process, what are and ?
The gas is returned to its initial state and again taken to the same final state but now through these two steps:
an isothermal compression to pressure and a volume increase to at constant pressure. What is for step and step ? What is for
step and step ? For the full process, what are and ?
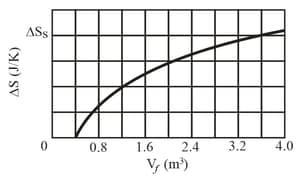
The cycle as shown in the figure represents the operation of a gasoline internal combustion engine. Volume . Assume the gasoline-air intake mixture is an ideal gas with What are the ratios (a), (b) , (c) , (d) and (e) ? (f) What is the engine efficiency?